Authors: Brendan Khong, Salvatore Ferlito, Stuart Quek, Gianluca Conte, Angelo Ingrassia, Jerome Rene Lechien, Carlos Chiesa-Estomba, Miguel Mayo, Antonino Maniaci, Thomas Radulesco, Justin Michel Nicolas Fakhry, and Riccardo Polosa
Published in: Ear, Nose & Throat Journal, Sage Journals, May, 2024.
Introduction
Oral leukoplakia is a significant clinical concern due to its association with a heightened risk of developing oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). The prevalence of oral leukoplakia in various populations underscores the importance of effective screening and early diagnosis. Traditional diagnostic methods, including visual examination and invasive tissue biopsies, often fall short in terms of sensitivity and specificity, leading to delays in intervention. This article presents a comprehensive review of emerging noninvasive diagnostic techniques, emphasizing their potential to enhance early detection and improve patient outcomes in oral oncology.
Design and Methods
The article employs a systematic review approach, synthesizing data from a variety of studies that investigate noninvasive diagnostic modalities for oral premalignant lesions. The review focuses on salivary biomarkers, particularly microRNAs, as well as various optical technologies, such as Raman spectroscopy, autofluorescence imaging, elastic scattering spectroscopy, and toluidine blue staining. The methodologies utilized in the reviewed studies include comparative analysis of diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, providing a thorough overview of the strengths and limitations of each technique.
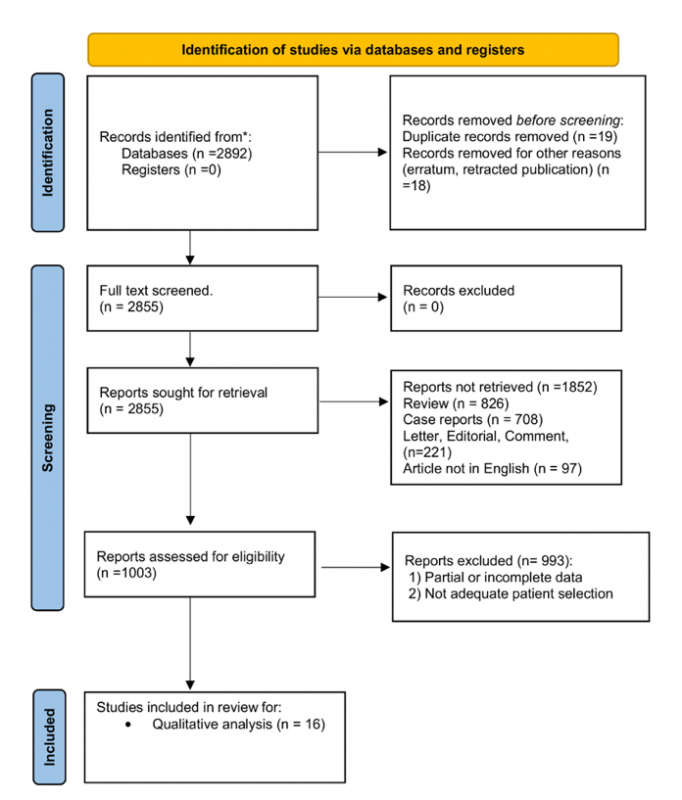
This flowchart illustrats the systematic approach used, following PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines.
What We Learned: Key Highlights
Salivary MicroRNA Analysis: Specific microRNAs, including miRNA-21 and miRNA-184, have demonstrated a strong correlation with oral cancer progression, indicating their potential utility as noninvasive biomarkers for early detection. Elevated levels of these microRNAs have been linked to the presence of OSCC and premalignant lesions.
Optical Technologies:
- Raman Spectroscopy: This technique has shown remarkable sensitivity, with studies reporting up to 100% accuracy in distinguishing malignant lesions from benign tissues. It provides real-time, in vivo analysis, making it a promising tool for clinical settings.
- Autofluorescence Imaging (AFI): AFI has proven effective in identifying dysplastic changes within the oral mucosa. With sensitivity reaching 100%, its specificity varies, necessitating further investigation to optimize its diagnostic accuracy.
- Toluidine Blue Staining: While this method has shown a sensitivity range between 77% and 100%, its specificity of 45% to 67% raises concerns regarding false positives, highlighting the need for supplementary diagnostic methods.
Microendoscopy: This advanced imaging technique provides high-resolution visualization of lesions, enabling real-time assessment of oral tissues. Its sensitivity ranges from 84% to 95%, with specificity between 91% and 95%, making it a valuable adjunct in the diagnostic process.
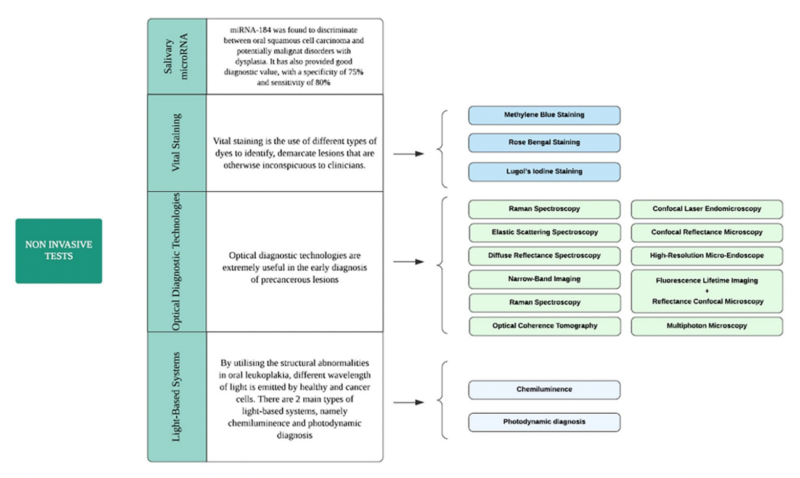
Above is presented the noninvasive test subclasses and main features.
Key Takeaways
- The review highlights the transformative potential of noninvasive diagnostic methods in the early detection of oral premalignant lesions, which could lead to timely interventions and improved prognoses for patients.
- Each diagnostic technique reviewed offers distinct advantages and limitations, necessitating a multi-modal approach to optimize patient screening and diagnosis. Combining methods may enhance overall diagnostic performance and reduce the reliance on invasive procedures.
- The promising results associated with salivary biomarkers and advanced optical technologies indicate a shift towards more patient-friendly diagnostic practices in oral oncology.
Future Directions
Future research should focus on validating the effectiveness of these noninvasive techniques across diverse populations to ensure broad applicability and reliability in clinical practice. Efforts should be directed towards developing standardized protocols that incorporate these diagnostic modalities into routine screenings for high-risk populations. Additionally, there is a need to explore novel biomarkers and refine existing technologies to enhance their diagnostic capabilities further. The integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence in analyzing diagnostic data could also provide new insights into early detection strategies, ultimately improving patient outcomes in oral cancer management.
Find other “Paper Alerts” on OncoDaily.


