Fresh from the stage at ESTRO 2025, Professor David Sebag-Montefiore presented the results of the ARISTOTLE trial, shedding new light on treatment strategies for locally advanced rectal cancer.
Background
Locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) with threatened or involved circumferential resection margins (CRM) represents a high-risk group for recurrence and poor outcomes. Pre-operative chemoradiotherapy (CRT) with capecitabine is a widely adopted standard approach. Preclinical data and early-phase trials have suggested that adding irinotecan to CRT may improve tumor response. The phase III ARISTOTLE trial was designed to test whether this combination translates into a survival benefit in MRI-defined high-risk LARC patients.
Methods and Study Design
ARISTOTLE is a randomized, open-label, multicenter phase III trial conducted across 75 UK sites between October 2011 and July 2018.
A total of 564 eligible patients were randomized
- CRT group (284): 45 Gy in 25 fractions + capecitabine 900 mg/m² BID on weekdays
- IrCRT group (280): Same radiotherapy dose + capecitabine 650 mg/m² BID weekdays + irinotecan 60 mg/m² IV weekly for 4 weeks
Most patients were male (66%) with a median age of 61 years (range 24–83). MRI staging showed mrT3 tumors in 77% and mrT4 in 16%; 49% had CRM involvement and 38% had margins ≤1 mm.
The median follow-up was 62.1 months.
Primary Endpoint
- Disease-free survival (DFS)
Secondary Endpoints:
- Loco-regional failure-free survival (LRFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), overall survival (OS), pathological complete response (pCR), R0 resection rate, toxicity, and post-surgical complications
Background
Locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) with threatened or involved circumferential resection margins (CRM) represents a high-risk group for recurrence and poor outcomes. Pre-operative chemoradiotherapy (CRT) with capecitabine is a widely adopted standard approach. Preclinical data and early-phase trials have suggested that adding irinotecan to CRT may improve tumor response. The phase III ARISTOTLE trial was designed to test whether this combination translates into a survival benefit in MRI-defined high-risk LARC patients.
Methods and Study Design
ARISTOTLE is a randomized, open-label, multicenter phase III trial conducted across 75 UK sites between October 2011 and July 2018.
A total of 564 eligible patients were randomized
CRT group (284): 45 Gy in 25 fractions + capecitabine 900 mg/m² BID on weekdays
IrCRT group (280): Same radiotherapy dose + capecitabine 650 mg/m² BID weekdays + irinotecan 60 mg/m² IV weekly for 4 weeks
Most patients were male (66%) with a median age of 61 years (range 24–83). MRI staging showed mrT3 tumors in 77% and mrT4 in 16%; 49% had CRM involvement and 38% had margins ≤1 mm.
The median follow-up was 62.1 months.
Primary Endpoint
Disease-free survival (DFS)
Secondary Endpoints:
Loco-regional failure-free survival (LRFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), overall survival (OS), pathological complete response (pCR), R0 resection rate, toxicity, and post-surgical complications
Results
In the largest randomized trial to date assessing irinotecan-enhanced chemoradiation in MRI-defined locally advanced rectal cancer, no significant improvement was seen in disease-free survival or other oncologic endpoints. The regimen was associated with increased toxicity and reduced compliance, undermining its potential benefit. These results indicate that capecitabine-based CRT remains the standard of care, and future research should explore more effective and tolerable strategies for intensification in high-risk rectal cancer.
Compliance
- High radiotherapy compliance in both arms (94% in iCRT, 98.6% in CRT).
- Lower chemotherapy compliance in the iCRT group (32% had <90% capecitabine dose compliance), compared to the CRT group (10%).
- Irinotecan compliance: 74% received >90% of irinotecan.
DFS Results
- iCRT arm: 68.3% at 3 years.
- CRT arm: 66.7% at 3 years.
No significant difference in DFS between both arms (HR 0.95, p=0.6).
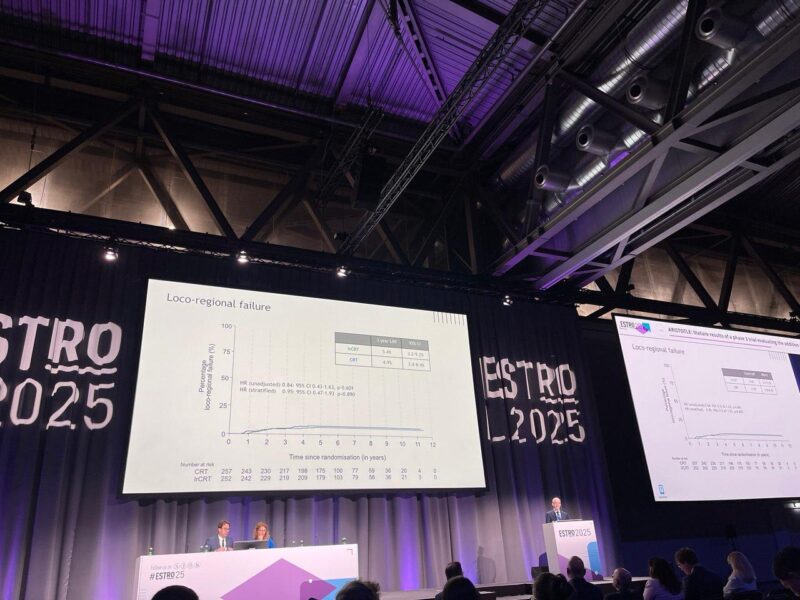
Loco-Regional Failure
- CRT group: 5.4% at 3 years.
- CRT group: 4.9% at 3 years.
No significant difference in loco-regional failure between groups.
Distant Metastasis and Overall Survival
- Distant Metastasis: No significant difference between the two groups.
- Overall Survival: Similar between arms with no statistical difference (HR 0.94, p=0.6).
Key Findings
- The addition of irinotecan did not improve DFS, pCR, or OS.
- IrCRT was associated with reduced treatment compliance for both radiotherapy and capecitabine.
- Irinotecan increased the risk of grade ≥3 toxicities, particularly diarrhea, neutropenia, and abdominal pain.
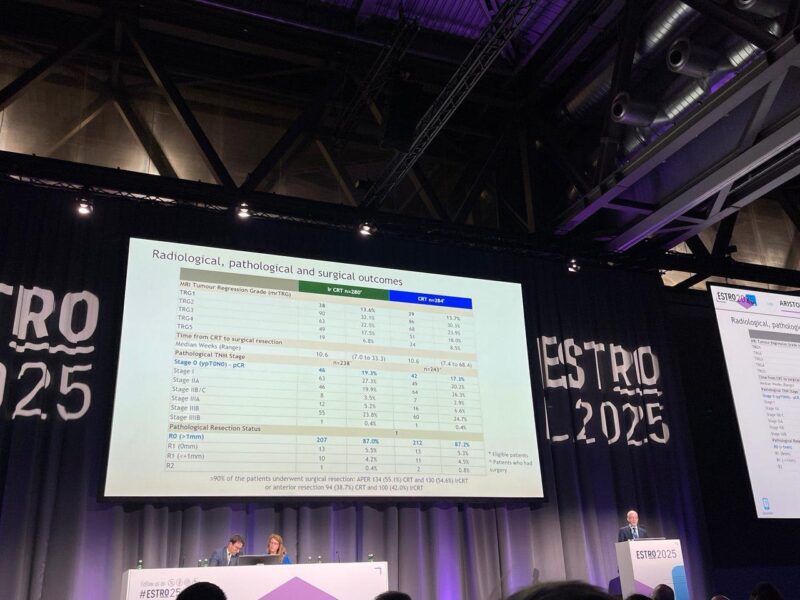
- R0 resection and complication rates were similar between arms, suggesting surgical outcomes were unaffected.
- Overall, survival and recurrence outcomes were not improved with the intensified regimen.
About ESTRO 2025
ESTRO 2025 brings together around 7,000 participants from over 80 countries, showcasing the latest research in clinical radiation oncology, radiobiology, medical physics, technology, and brachytherapy. Leading doctors and scientists from around the world present groundbreaking findings, in line with the conference theme: “Transformative innovation through collaboration”. ESTRO 2025 is the annual congress of the European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO), an organisation dedicated to advancing cancer treatment through radiotherapy and multimodal approaches. ESTRO promotes education, science, and research and advocates for universal access to radiotherapy. With nearly 10,000 members worldwide, it supports radiation oncology professionals and the broader oncology community in their daily practice.
Read ESTRO 2025 Updates on OncoDaily.