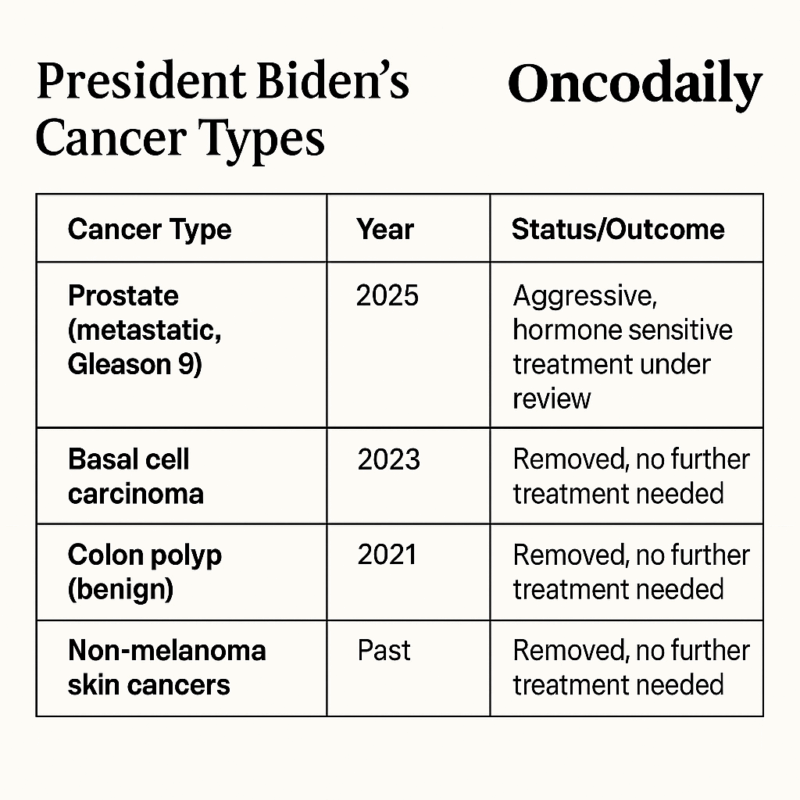
Joe Biden, the former U.S. president, was diagnosed in May 2025 with an aggressive form of prostate cancer that has metastasized (spread) to his bones-a development that marks a serious escalation in his health status at age 82. The diagnosis followed a routine physical exam where a small nodule was detected in his prostate. He had also been experiencing increasing urinary symptoms, which prompted further evaluation and a biopsy.

Photo: Depositphotos
How Was President Joe Biden Diagnosed with Prostate Cancer?
Biden’s prostate cancer is characterized by a Gleason score of 9 (Grade Group 5), which is the highest category on the Gleason scale and indicates a very aggressive, fast-growing, and potentially life-threatening cancer. The cancer’s spread to the bone (metastasis) makes it more challenging to treat compared to localized prostate cancer. Despite the severity, his medical team noted that the cancer appears to be hormone-sensitive, meaning it may respond well to hormone therapy, which is a cornerstone of treatment for advanced prostate cancer.
What Is President Joe Biden’s Current Cancer Status and Treatment Plan?
Biden and his family are currently reviewing treatment options with his physicians. While no specific regimen has been publicly announced, hormone therapy is likely to be a key part of his management plan due to the hormone-sensitive nature of the disease. There have been no reports of treatment-related complications, and further updates are expected as his team continues to evaluate the best course of action.

From X of Justin Trudeau
Joe Biden’s Health History
President Joe Biden has faced multiple cancer-related diagnoses over the years. In 2023, a basal cell carcinoma—a common, non-metastatic form of skin cancer—was removed from his chest, with all cancerous tissue successfully excised and no further treatment needed. In 2021, he had a benign but potentially pre-cancerous polyp removed from his colon. He has also undergone treatment in the past for several non-melanoma skin cancers.
What was the Prognosis ?
Prostate cancer is common among older men, but the prognosis depends heavily on the stage and aggressiveness at diagnosis. Localized prostate cancer has a high survival rate, but metastatic, high-Gleason-score disease is much more difficult to treat and carries a lower long-term survival rate. The fact that Biden’s cancer is hormone-sensitive offers some hope for disease control, but the outlook remains guarded due to the advanced stage.
Public and Political Impact
Biden’s diagnosis has come shortly after he left office and amid ongoing public interest in the health of American leaders. His health has been under scrutiny, especially following his decision to step down from the 2024 presidential race. Biden has been a prominent advocate for cancer research, notably leading the “Cancer Moonshot” initiative during his vice presidency and presidency.
You Can Also Read Rudy Giuliani and Prostate Cancer: How He Went Against, How He Survived, and More by Oncodaily

What Causes Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer risk is influenced by genetic factors, age, hormonal imbalances, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors. Key risk elements include a family history of cancer, older age, higher testosterone levels, poor diet, and obesity. Geographic variations also suggest environmental influences. Prevention strategies involve maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management. Genetic testing and individualized screening are recommended for those with higher risk profiles.
Genetic and Hormonal Factors
Genetics and hormonal factors play significant roles in influencing prostate cancer risk. Here’s a detailed look at these influences:
- Family History: Men with a family history of prostate cancer are at higher risk. Studies show that having a first-degree relative (father, brother) with prostate cancer increases the risk by about 2-3 times (: American Cancer Society, Prostate Cancer Risk Factors).
- Inherited Mutations: Genetic mutations, such as those in the BRCA2 gene, are linked to a higher risk of prostate cancer. Men with BRCA2 mutations are about 2-3 times more likely to develop prostate cancer compared to those without these mutations ( National Cancer Institute, Genetics of Prostate Cancer).
- Lynch Syndrome: This genetic disorder, associated with several types of cancer, also increases the risk of prostate cancer. Men with Lynch Syndrome have a lifetime risk of about 7-12% ( Genetics Home Reference, Lynch Syndrome).
- High Testosterone: Elevated levels of testosterone are linked to a higher risk of prostate cancer. Research suggests that high testosterone can promote the growth of prostate cancer cells. However, the relationship between testosterone levels and prostate cancer risk remains complex and under ongoing study ( Mayo Clinic, Prostate Cancer Risk Factors)
- Androgen Receptor Gene: Variations in the androgen receptor gene, which regulates the effects of testosterone, are associated with increased prostate cancer risk. Studies have shown that specific gene variants can modify the risk ( Journal of Clinical Oncology, Androgen Receptor Gene Variants and Prostate Cancer Risk).
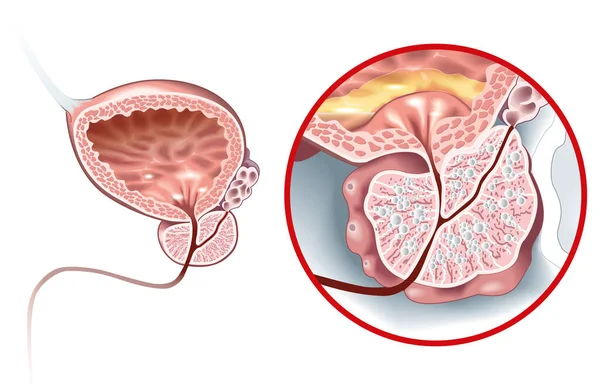
Healty prostate and prostate with cancer Photo: Depositphotos
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
A diet high in red meat and processed foods is linked to a 20% increased risk of prostate cancer (American Institute for Cancer Research). In contrast, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may reduce this risk (Journal of the National Cancer Institute). Regular exercise can lower the risk by 10-30% (Journal of Clinical Oncology). Smoking increases the likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, with smokers about 30% more likely to develop it compared to non-smokers. Additionally, exposure to certain chemicals, like pesticides, may increase risk, though this is still being studied (Environmental Health Perspectives).
How Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented?
Preventive measures for cancer focus on regular screenings, lifestyle adjustments, and dietary changes. Routine medical tests help detect cancers early, while quitting smoking and staying physically active lower risk factors. A diet rich in plant-based foods, along with limiting alcohol and red meat, is advised by cancer research organizations to reduce cancer incidence.
Regular Screenings and Early Detection
Regular PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) tests and screenings are essential for early detection of prostate cancer, particularly for men over 50 or those with a family history of the disease. PSA tests measure the level of a specific protein in the blood, and elevated levels can indicate prostate issues, including cancer.
Recognizing early symptoms, such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination (especially at night), or blood in the urine, is crucial. Early-stage prostate cancer often shows minimal symptoms, making regular screenings even more vital. Prompt medical consultation at the first sign of symptoms can lead to early diagnosis, improving treatment outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
You Can Learn More About Latest Research In Prostate Cancer Watching ASCO updates by OncoDaily
Lifestyle Changes
To reduce the risk of prostate cancer, maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats while limiting red and processed meats. Foods like tomatoes, broccoli, and omega-3-rich fish are linked to lower risk (American Institute for Cancer Research). Regular exercise, aiming for at least 30 minutes most days, helps regulate hormones, reduce inflammation, and maintain a healthy weight (Journal of Clinical Oncology). Avoiding smoking is crucial, as it is associated with aggressive prostate cancer, and quitting improves overall health (Cancer Research UK). Lastly, limit alcohol consumption to moderation—up to one drink per day for men (American Cancer Society).
Dietary Recommendations
Incorporating antioxidants and fiber-rich foods can help reduce prostate cancer risk. Tomatoes, high in lycopene, may lower risk by up to 35% (National Cancer Institute). Berries are rich in antioxidants that combat cell damage, while fiber-rich whole grains like brown rice and oats are linked to lower cancer risks (American Institute for Cancer Research).
Legumes, such as beans and lentils, provide fiber and phytoestrogens that may inhibit cancer growth. Healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish, can reduce the risk of prostate cancer death by 26% (Harvard Medical School). Nuts and seeds offer additional healthy fats and fiber, and green tea contains catechins that inhibit cancer growth (UCLA). Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower also have protective effects against cancer (Johns Hopkins Medicine).
You Can Also Read In Memory of Jimmy Carter and His Battle with Melanoma by Oncodaily

Written by Aharon Tsaturyan MD
FAQ
What type of prostate cancer was Joe Biden diagnosed with?
Joe Biden was diagnosed with an aggressive form of prostate cancer characterized by a Gleason score of 9 (Grade Group 5), indicating a high-grade, fast-growing tumor that has metastasized to his bones.
What does it mean that Biden’s prostate cancer is hormone-sensitive?
Hormone-sensitive prostate cancer means the cancer cells rely on male hormones (androgens) like testosterone to grow. This allows doctors to use hormone therapy to reduce hormone levels and control the cancer’s progression effectively.
How advanced is Biden’s prostate cancer?
His cancer is classified as metastatic (Stage 4) because it has spread beyond the prostate to the bones. This stage is considered incurable but manageable with current treatments.
What symptoms led to Biden’s diagnosis?
Biden experienced increasing urinary symptoms, and during a routine exam, a small nodule was found on his prostate, prompting further evaluation and diagnosis.
What treatment options are available for Biden’s prostate cancer?
Treatment likely includes hormone therapy to block testosterone production, possibly combined with androgen blockers, chemotherapy, or radiation depending on disease extent. His medical team is currently reviewing options.
What is the prognosis for someone with metastatic prostate cancer like Biden?
Advances in treatment mean patients can live many years after diagnosis. Survival varies widely, from under a year in the most aggressive cases to 10 or more years in others. Experts are hopeful Biden could live a prolonged life with effective management.
What type of skin cancer did President Biden have removed in 2023?
In February 2023, President Biden had a basal cell carcinoma, the most common form of skin cancer, removed from his chest. All cancerous tissue was successfully excised, and no further treatment was required.
How serious is basal cell carcinoma and does it spread?
Basal cell carcinoma is generally slow-growing and rarely metastasizes (spreads) to other parts of the body. It is highly curable when detected early and usually treated with minor surgical procedures.
Has President Biden had other skin cancers in the past?
Yes, President Biden has had several non-melanoma skin cancers removed before his presidency. He continues regular dermatologic surveillance to monitor for new lesions
