The vaping epidemic has reached alarming levels, with 14.1% of young adults aged 18 to 25 actively vaping—approximately 4.7 million individuals in this demographic alone. As health concerns escalate, particularly regarding the potential link between vaping and lung cancer, it is crucial to address widespread misinformation. Does Vaping Cause Lung Cancer? Recent studies reveal that combining vaping with cigarette smoking significantly increases lung cancer risk, with individuals who do both being four times more likely to develop the disease than those who only smoke. This introduction highlights the urgent need to clarify vaping’s health impacts and present the latest research findings to combat this growing public health issue.
Does Vaping Cause Lung Cancer?
The relationship between vaping and lung cancer remains under investigation, with no definitive evidence yet establishing a direct causal link. However, recent studies suggest potential risks associated with vaping due to the presence of harmful chemicals in e-cigarette vapor.
E-cigarettes contain nicotine derivatives, heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and aldehydes, which are known carcinogens or potential oncogens. These compounds can arise from both the e-liquid itself and the pyrolysis of components during vaping. Dara Bracken-Clarke Lung Cancer . 2021 Mar
Research indicates that combining vaping with smoking significantly increases lung cancer risk. For instance, individuals who both vape and smoke have a fourfold higher risk of lung cancer compared to those who only smoke cigarettes. M A Bittoni J Oncol Res Ther 2024
Both cigarette smoking and e-cigarette use induce epigenetic changes that are predictive of carcinogenesis. These changes have been observed in e-cigarette users with limited smoking history, suggesting potential long-term risks. Chiara Herzog Cancer Res . 2024
Despite these findings, the long-term effects of vaping on lung cancer risk remain unclear. Given the lag time between exposure and cancer development, typically spanning decades, more extensive and long-term studies are necessary to fully understand the impact of vaping on lung health. The current evidence underscores the importance of continued research and caution in recommending e-cigarettes as a harm reduction strategy without comprehensive safety data.
How Does Vaping Affect Lung Health?
Vaping affects lung health both immediately and potentially over time, posing significant risks. Immediately, vaping can cause acute respiratory changes, including increased airway resistance, breathing difficulty, and transient decreases in oxygen saturation. Lucy Honeycutt, Nature 2022
The EVALI outbreak highlighted severe lung injuries linked to vaping, with symptoms like pneumonia and bronchiolitis. Fakher Rahim Cureus. 2024
Long-term risks include potential associations with chronic lung diseases such as COPD and emphysema, as suggested by studies linking nicotine and vaping to these pathologies. Ventilation abnormalities in EVALI patients have persisted for months, indicating lasting impacts on lung function. Joseph J. Hofmann Front. Med. 2024
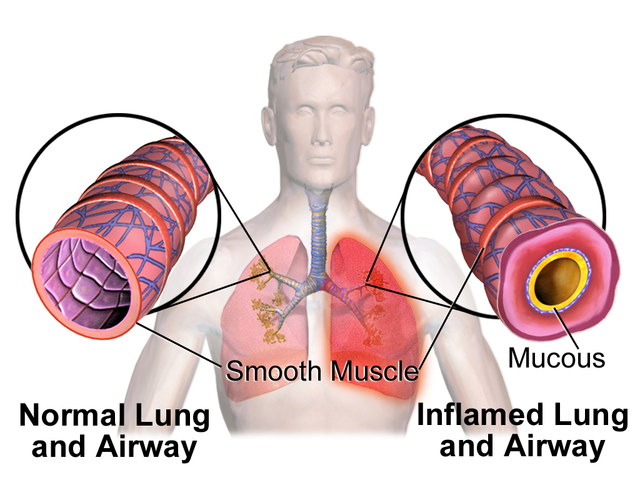
Despite these findings, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of vaping on lung health, as current studies are limited by their small size and short duration.
Exposure to Harmful Chemicals
E-cigarette vapor contains a variety of harmful chemicals, including formaldehyde, acrolein, and other carcinogenic compounds. Formaldehyde, a known carcinogen, can form when e-liquids overheat or during “dry-puff” conditions, significantly exceeding occupational safety limits. Acrolein, primarily used as a herbicide, is also present in e-cigarette emissions and can cause lung disease. While benzene is not frequently mentioned in the context of e-cigarette emissions, other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals like nickel and lead are commonly found.
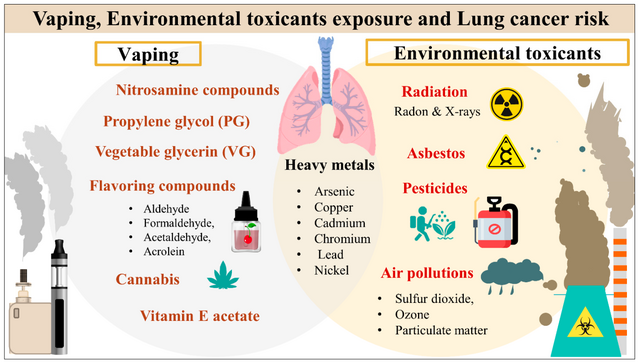
Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Vaping can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation in the lungs, contributing to cellular damage and potentially creating a cancer-friendly environment. This process involves the inhalation of e-cigarette aerosols, which contain reactive oxygen species (ROS) and aldehydes that induce oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine production, even in the absence of nicotine. Studies have shown that acute exposure to e-cigarette aerosol increases markers of oxidative stress and inflammation in human subjects, such as C-reactive protein and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule (sICAM), peaking within 1-2 hours and returning to baseline levels after 6 hours. Shampa Chatterjee American Journal of Physiology 2019
In animal models, e-cigarette exposure has been linked to increased levels of inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α, as well as neutrophil infiltration and NF-κB pathway activation, which are indicative of acute lung inflammation. Tiancong Ma Arch Toxicol. 2020
Furthermore, cannabis vaping has been shown to elicit transcriptomic and metabolomic changes in human bronchial epithelial cells, affecting pathways related to inflammation, oxidative stress, and cancer. Maddison T Arlen Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol . 2025
Chronic exposure to e-cigarette aerosols could exacerbate these effects, potentially leading to sustained inflammation and oxidative stress that may contribute to a cancer-friendly environment in the lungs.
Effects on Immune Response in Lungs
Vaping can weaken the lung’s natural immune defenses by inducing widespread inflammation and disrupting immune cell function. Electronic cigarette aerosol (ECA) impairs neutrophil chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and oxidative burst, while increasing macrophage and dendritic cell recruitment and activation. This disruption compromises the epithelial barriers, making the lungs more susceptible to bacterial and viral infections. Studies have shown enhanced biofilm formation in bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae, and impaired antiviral responses against pathogens such as influenza A and SARS-CoV-2. Katarzyna Zima Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 Feb
Furthermore, vaping modulates adaptive immunity, affecting T and B cell function and increasing systemic inflammatory markers. These immunological disruptions can lead to heightened risks for chronic inflammatory diseases and respiratory infections. The long-term consequences include increased susceptibility to infections and potentially autoimmune conditions, posing a significant public health challenge. Overall, vaping’s impact on lung immunity not only makes it harder for the body to repair damage but also increases the risk of severe infections and chronic diseases.

Has Anyone Gotten Lung Cancer from Vaping?
Despite the growing concern about vaping’s potential link to lung cancer, there are currently no documented cases directly attributing lung cancer to vaping alone. This lack of evidence is largely due to the long latency period of cancer development, which typically spans decades. Since vaping has only recently become widespread, it may take years or even decades to fully understand its long-term health impacts, including any potential link to lung cancer.
The challenges in drawing conclusions are compounded by the fact that many studies focus on acute or short-term effects rather than long-term outcomes. For instance, the outbreak of E-cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury (EVALI) in 2019 highlighted the short-term risks of vaping, with over 2,500 cases reported, primarily affecting young males using THC-containing products. Shaimaa A Shehata Cancers (Basel). 2023
While EVALI demonstrates the immediate dangers of vaping, such as severe lung inflammation and injury, it does not provide insight into the long-term cancer risk.
Animal studies have shown that vaping can induce lung cancer in mice, suggesting potential carcinogenic effects. However, translating these findings to humans requires more extensive and long-term research. Until such studies are conducted, the direct link between vaping and lung cancer remains speculative, though the presence of carcinogenic compounds in e-cigarette aerosols raises significant concerns about potential future risks.
Comparing Vaping and Smoking: Which Is Safer?
When comparing the health risks of vaping versus smoking, it is generally accepted that vaping poses fewer risks than smoking, particularly in terms of exposure to toxic chemicals. Smoking involves the combustion of tobacco, releasing over 7,000 chemicals, many of which are carcinogenic and contribute to conditions like lung cancer and heart disease. In contrast, vaping involves heating e-liquids, which contain fewer toxicants but still pose significant health risks, including respiratory issues and potential carcinogenic effects.

The carcinogenic risk associated with smoking is well-documented, significantly increasing cancer risk, while vaping’s long-term carcinogenic effects are less clear but potentially concerning due to the presence of carcinogens like formaldehyde. Both vaping and smoking can cause lung irritation and increase the risk of respiratory diseases. Vaping has been linked to severe lung injuries, such as EVALI, and conditions like “popcorn lung.” Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke, and vaping also poses cardiovascular risks, including increased risk of heart disease and stroke, though the mechanisms may differ.
For those considering vaping as a smoking alternative, it is crucial to understand that while vaping may be less harmful than smoking, it is not without risks. The long-term effects of vaping are still being studied, and its safety as a cessation tool remains debated. If quitting nicotine entirely is not feasible, switching to vaping might reduce exposure to some toxicants, but it should not be seen as a completely safe option. Ultimately, the safest choice is to avoid both smoking and vaping altogether.
Potential Benefits for Smoking Cessation
Vaping can serve as a harm reduction tool for individuals attempting to quit smoking, particularly when used under medical supervision and as a short-term strategy. Studies have shown that e-cigarettes can be more effective than traditional nicotine replacement therapies (NRT) in aiding smoking cessation, with some research indicating that e-cigarette users have higher quit rates compared to those using NRTs. For instance, a study in the UK found that smokers using e-cigarettes had double the quit rates of those using NRTs when accompanied by behavioral support.
However, it is crucial to view vaping as a transitional tool rather than a long-term habit. While vaping is generally considered less harmful than smoking, it still poses health risks, including respiratory issues and potential long-term effects that are not yet fully understood. Therefore, vaping should be used under medical guidance to minimize risks and ensure that it is part of a comprehensive plan to eventually cease nicotine use altogether.
You Can Also Listen Does Processed Meat Cause Cancer? Myths and Facts: OncoDaily DeepDive
Vaping is often seen as a safer alternative to smoking, but several misconceptions surround its health risks. While many believe nicotine is the only concern, vapes contain harmful chemicals like formaldehyde and acrolein, which can damage the lungs and heart. Another misconception is that lung damage from vaping is reversible, but some effects, such as lung scarring and inflammation, may be permanent.
Contrary to popular belief, vaping is not just harmless water vapor—e-cigarette aerosol contains toxic substances, including heavy metals and volatile organic compounds. Although some use vaping to quit smoking, many end up continuing both habits, increasing health risks rather than eliminating them. Additionally, teen vaping is often dismissed as a minor issue, but nicotine addiction can harm brain development and raise the risk of future substance use. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed decisions about vaping.
Myth: Nicotine Is the Only Risk in Vaping
Flavorings, solvents, and other additives in vaping liquids can produce harmful byproducts when heated, posing significant health risks. For instance, diacetyl, a common flavoring agent, is linked to bronchiolitis obliterans, also known as “popcorn lung,” a condition characterized by scarring in the small airways of the lungs. Other flavoring additives like 2,3-pentanedione and vanillin have also been shown to induce pulmonary toxicity.
When e-liquids are heated, they can release toxic carbonyl compounds such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde, which are classified as carcinogenic or potentially carcinogenic to humans. These chemicals can cause oxidative stress and inflammation in lung cells, contributing to respiratory issues and potentially increasing cancer risk. Additionally, the pyrolysis of e-liquids can transform additives into more toxic substances, similar to how vitamin E acetate was linked to severe lung injuries during the EVALI outbreak. Akihiro Kishimoto Nature 2024
Overall, the heating of vaping liquids can lead to the formation of harmful byproducts that pose serious health risks.
Myth: Lung Damage from Vaping Is Reversible
While some lung inflammation caused by vaping may improve over time, long-term damage, particularly from chronic use, may not be reversible. Research has shown that vaping can lead to scarring and cellular damage in the lungs. For instance, the outbreak of e-cigarette or vaping product use-associated lung injury (EVALI) highlighted severe lung damage, including diffuse alveolar damage and organizing pneumonia, which can result in lasting health impacts if not promptly diagnosed and treated. Jin-Ah Park Annu Rev Physiol. 2023
Studies have demonstrated that chronic vaping can alter lung function and structure, potentially leading to irreversible changes. Histological examinations of lung biopsies from vapers have revealed acute to subacute lung injury, including fibroblast plugs, hyaline membranes, and interstitial organization, indicating significant cellular damage. Furthermore, some cases of EVALI have shown that if left untreated, the condition can lead to irreversible lung injury. These findings underscore the importance of understanding the long-term risks associated with vaping and the need for caution in its use. Kathryn B Vess Cureus 2024.
How to Reduce Potential Risks Associated with Vaping
Vaping is often marketed as a safer alternative to smoking, but it still carries potential health risks. While eliminating vaping altogether is the best option, individuals who choose to vape or are transitioning from smoking can take steps to minimize harm.
Use Reputable Products
Avoid counterfeit or black-market e-cigarettes and e-liquids, as they may contain harmful contaminants or additives. Always purchase from reputable manufacturers and retailers to ensure compliance with safety standards. In regions like the EU and UK, e-cigarettes are regulated for nicotine concentration, packaging, and labeling—ensure products meet these standards.
Avoid High-Temperature Settings
Using devices at lower power settings can help minimize the formation of toxic compounds, as higher temperatures can cause e-liquids to break down into more harmful substances. Additionally, be mindful of nicotine consumption to prevent poisoning, as moderation is key to safer vaping.
Consider Smoking Cessation Programs
For those transitioning from smoking to vaping as a cessation strategy, consulting healthcare professionals is crucial. They can provide guidance on reducing nicotine intake and eventually quitting vaping. Utilize available smoking cessation resources, such as local health services or programs like the NHS Stop Smoking Service in the UK.
Safer Usage Practices
Regularly clean and maintain vaping devices to prevent bacterial growth and contamination. Avoid overheating by not leaving devices unattended while charging and ensuring proper ventilation during use. Keep up with regulatory updates on vaping products in your region and stay aware of potential health risks, including respiratory issues and long-term effects still being studied.
By following these guidelines, individuals can reduce the risks associated with vaping while working toward a healthier lifestyle. However, the safest option remains avoiding both smoking and vaping altogether.
You Can Also Read Does 5G Mobile Network Cause Cancer? Myths and Facts by OncoDaily
Vaping and Environmental Damage
Vaping poses significant environmental challenges, contributing to pollution and waste management issues. One major concern is air pollution and climate change. Vaping produces emissions that contribute to air pollution and climate change. The aerosol from e-cigarettes contains ultrafine particles and volatile organic compounds that can create ozone, impacting air quality.
Disposable vapes are a major source of hazardous waste, including plastics, electronics, and chemical waste. These devices contain heavy metals like lead and mercury, which can leach into soil and water when improperly disposed of. This not only contaminates the environment but also poses risks to wildlife.
Vape waste, particularly microplastics from broken-down devices, can harm marine life and contaminate waterways. These microplastics are consumed by animals and have been found in the food chain, highlighting the need for better waste management practices.

Arnaut Blowing Smokeat the Nose of His Dog. Jean Leon Gerome, oil on canvas 73 x 6o sm. 1882
A significant issue is the lack of proper disposal methods for vape devices. Many users do not know how to dispose of them correctly, leading to littering and improper recycling. This lack of guidance from manufacturers exacerbates the environmental impact.
The production and transportation of vape products also contribute to a significant carbon footprint, further impacting climate change. To mitigate these environmental impacts, it’s crucial to develop effective recycling programs and educate users on proper disposal methods. Additionally, reducing vape use or transitioning to more sustainable alternatives can help minimize environmental damage.
Vape Bombs?
Vapes can cause burns and damage through several mechanisms. One of the most dangerous risks is battery explosions. Defective e-cigarette batteries can lead to fires and explosions, resulting in severe burns. These incidents often occur when devices are improperly charged or when batteries are damaged. Explosions can happen in pockets, hands, or faces, causing significant injuries.
Thermal injuries are another concern. The high temperatures generated by vape devices can cause burns to the mouth, tongue, and surrounding areas. These injuries can be painful and may require medical attention.
Exposure to e-liquids can also lead to chemical burns or irritation, particularly if the liquid comes into contact with the skin or eyes. Nicotine toxicity symptoms include vomiting, nausea, and skin irritation.

Long-Term Research and Unknowns
The relative novelty of vaping has led to significant gaps in current research, particularly regarding its long-term health effects. One of the major challenges is the lack of long-term data on vaping’s impact on lung health and cancer risk. Most studies have focused on short-term effects, leaving a need for comprehensive investigations that span several years.
Additionally, many studies face methodological challenges. For instance, the “stock-flow” problem can lead to biased results, as cohorts may exclude those who have already quit smoking due to vaping. The debate over whether vaping acts as a gateway to smoking also remains contentious, with mixed evidence and a need for more robust studies.
Ongoing research is addressing these gaps. For example, a landmark UK study will investigate the long-term health effects of vaping on young people, tracking 100,000 participants over a decade to understand its impact on health and wellbeing. Another significant study, funded by the National Institutes of Health, aims to provide detailed insights into how long-term vaping affects cardiovascular and pulmonary health.
Recent reviews highlight the need for rigorous clinical trials to assess the cancer risk associated with vaping, as current evidence is limited and inconclusive. These ongoing studies aim to fill the gaps in current research by providing more comprehensive and long-term data on vaping’s health impacts.
Written by Aharon Tsaturyan, MD
FAQ
Can vaping help you quit smoking?
There is growing evidence that vaping can help some people quit smoking. Electronic cigarettes are considered a legitimate tobacco harm reduction tool for smokers who are unable or unwilling to quit using conventional methods.
Are e-cigarettes safer than regular cigarettes?
E-cigarettes are generally considered less harmful than regular cigarettes, though they are not risk-free. They contain fewer toxic chemicals than tobacco smoke, but long-term health effects are still being studied
What are the immediate health risks of vaping?
Immediate health risks include irritation of the mouth and airways, persistent coughing, nausea, vomiting, chest pain, and palpitations. Nicotine poisoning can occur from inhaling too much nicotine or ingesting e-liquid, leading to symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and changes in heart rate.
Can vaping cause long-term health issues?
Yes, vaping can lead to long-term health issues such as respiratory problems, permanent lung damage, and potential cardiovascular risks. Chemicals in vape aerosols, like formaldehyde and acetaldehyde, are linked to lung disease and heart disease. Additionally, vaping can harm brain development, particularly in adolescents.
Is vaping associated with severe lung conditions?
Yes, vaping has been linked to severe lung conditions, notably EVALI (e-cigarette, or vaping, product use-associated lung injury). This condition can cause life-threatening lung injuries and has been associated with vitamin E acetate in some e-liquids, particularly those containing THC.
Does vaping increase the risk of lung cancer?
While vaping itself has not been conclusively linked to lung cancer in non-smokers, there is growing evidence that it exposes users to carcinogenic chemicals, which could potentially increase cancer risk over time. However, studies suggest that combining vaping with smoking significantly increases lung cancer risk compared to smoking alone.
Is vaping and smoking together more harmful for lung cancer risk than smoking alone?
Yes, research indicates that people who both vape and smoke are at a higher risk of developing lung cancer than those who only smoke. Studies have shown that this combination can increase lung cancer risk by as much as four times compared to smoking alone. This increased risk is attributed to the cumulative exposure to harmful chemicals from both sources.
What are the health risks associated with smoking?
Smoking poses significant health risks, including increased chances of developing lung cancer, heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Cigarette smoke contains over 4,000 chemicals, many of which are carcinogenic. Smoking harms nearly every organ in the body and is the leading cause of preventable deaths worldwide.
How can quitting smoking improve my health?
Quitting smoking offers numerous health benefits. Within 20 minutes of quitting, blood pressure and pulse rate return to normal. After 24 hours, the body eliminates carbon monoxide, and within a few weeks, lung function improves. Quitting before age 50 can reduce the risk of dying from smoking-related diseases by 50%, and after 10 years, the risk of lung cancer is halved compared to continuing smokers.


