Flash Radiotherapy (Flash-RT) is a novel experimental cancer treatment that employs ultra-high dose rates of radiation delivered in short bursts, typically under 200 milliseconds. This innovative approach has captured the attention of the oncology community for its potential to achieve comparable—or even superior—therapeutic outcomes to conventional radiotherapy while significantly reducing side effects.
Unlike traditional radiotherapy, which involves multiple treatment sessions over several weeks, Flash-RT administers radiation in a fraction of the time. The result is a potentially more tolerable treatment option for patients, with fewer toxicities and faster recovery times. Preclinical studies and early trials have shown promising results across various cancer types, including lung, breast, and superficial tumors.
What Is Flash Radiotherapy?
Flash radiotherapy is a novel cancer treatment that utilizes high-dose radiation delivered at ultra-fast speeds, achieving a mean dose rate greater than 40 Gy/s in delivery times of less than 200 milliseconds. This innovative technique is designed to deactivate cancer cells by inducing critical DNA breaks through high-energy ionizing radiation. The main objective of flash radiotherapy is to effectively target cancer cells while protecting healthy tissues from unnecessary radiation damage.
How Does Flash Radiotherapy Work?
Flash radiotherapy achieves dose rates exceeding 40 Gy/s within a delivery time of under 200 milliseconds. This rapid administration of radiation creates a unique biological effect that differentiates it from conventional methods. The high dose rates utilized in flash radiotherapy induce critical DNA damage in cancer cells, effectively deactivating them. The immediate and concentrated application of radiation enhances the treatment’s antitumor efficacy. One of the key features of flash radiotherapy is its ability to protect surrounding healthy tissues. Traditional radiotherapy often causes collateral damage to adjacent normal cells, leading to significant side effects and toxicity. In contrast, flash radiotherapy’s ultra-fast delivery minimizes the exposure time for healthy tissues, thereby reducing the likelihood of radiation-induced injury.
Flash radiotherapy is associated with transient hypoxia, where the rapid delivery of radiation depletes oxygen in the targeted area. This phenomenon enhances the radiation’s effectiveness while also contributing to the sparing of normal tissues.
What Are the Main Types of Flash Radiotherapy?
Flash radiotherapy, an experimental approach, includes three main types: Linear Electron Accelerators (LINAC), which use high-energy electron beams to deliver radiation. Proton Therapy Systems, which leverage protons for enhanced dose distribution and tumor targeting with minimal impact on surrounding tissues and Electron-Based Flash Therapy, which employs electron beams to treat surface tumors rapidly and effectively while reducing exposure to deeper healthy tissues.
Photon-based Flash Radiotherapy
Photon-based flash radiotherapy employs high-energy X-rays (photons) administered at extremely high dose rates to induce the FLASH effect. The technique involves utilizing high-energy photons, which have the ability to penetrate deeply into tissues. This property allows for effective targeting of various types of cancers, including those located in the lung, breast, and gastrointestinal tract.
Electron-based Flash Radiotherapy
Electron-based flash radiotherapy is emerging as a viable alternative for the treatment of superficial cancers, including skin cancer. This modality takes advantage of the unique properties of electron beams, which have limited penetration depths, making it particularly suitable for targeting surface-level tissues. Electron-based flash radiotherapy is specifically designed for cases where the treatment is confined to areas near the skin surface. This makes it ideal for addressing superficial tumors, allowing for effective treatment while minimizing impact on deeper tissues.
The technique utilizes high-energy electron beams, which deliver radiation doses at ultra-high rates. This rapid delivery is integral to achieving the FLASH effect, potentially enhancing tumor control while offering protection to surrounding healthy tissues.
As research progresses, electron-based flash radiotherapy is poised to offer a novel treatment pathway for patients with superficial cancers. The potential benefits of decreased acute skin reactions not only improve patient comfort but may also enhance overall treatment adherence and satisfaction.
Flash Radiotherapy Side Effects: What Should You Expect?
A major advantage of Flash-RT is its capacity to target cancer cells precisely while sparing surrounding healthy tissues. This focused approach reduces the incidence of common radiation-related side effects, like skin irritation and damage to nearby organs. Flash-RT’s reduced toxicity profile allows many patients to experience quicker recovery times, which can greatly enhance their quality of life. With shorter recovery periods, patients are often able to return to their daily routines sooner and with minimal disruption.
Common Side Effects
Some patients may notice changes in skin texture or sensitivity at the treatment site. To manage skin irritation, it is recommended to keep the affected area clean and dry, apply gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers to soothe the skin, and avoid direct sunlight on the treated area. Although nausea is less common with Flash-RT, it can still occur. Relief may be found by eating small, frequent meals, staying hydrated, and using natural remedies like ginger or peppermint.
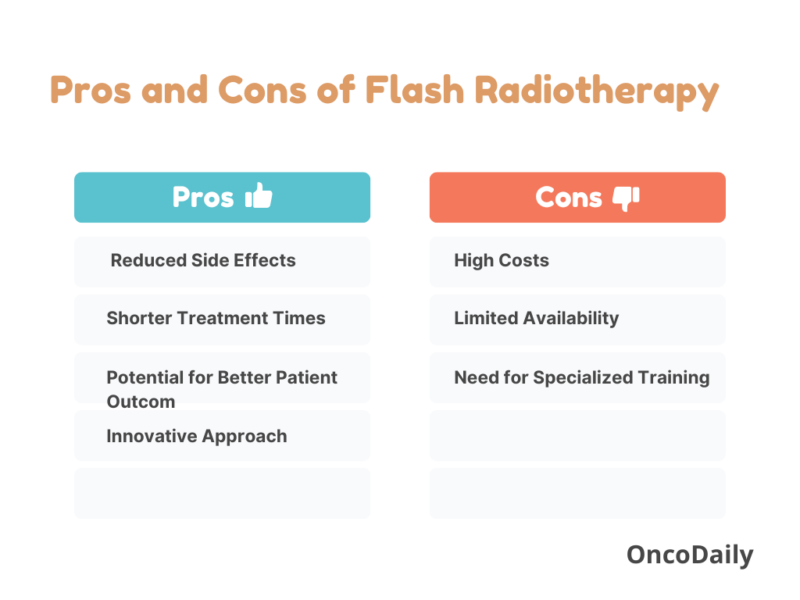
Pros and Cons of Flash Radiotherapy
Flash radiotherapy (Flash-RT) is gaining attention in the field of oncology due to its unique approach and promising outcomes. However, like any medical advancement, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. A balanced discussion of these aspects is crucial for understanding its role in cancer treatment.
Benefits of Flash Radiotherapy
Flash-RT demonstrates strong potential to reduce the side effects commonly seen with conventional radiotherapy. By precisely targeting cancer cells and sparing nearby healthy tissues, it often leads to less skin irritation and organ damage, thereby enhancing patients’ overall quality of life. A key advantage of Flash-RT is its ultra-fast delivery of high-dose radiation, which not only shortens each treatment session but may also reduce the overall number of therapy visits needed. This approach offers greater convenience and saves time for patients.
Flash-RT marks a significant advancement in radiation oncology, challenging traditional fractionation concepts and providing a novel approach to enhance therapeutic efficacy.
Limitations of Flash Radiotherapy
Despite its potential, Flash-RT is still regarded as an experimental treatment. Ongoing clinical trials are essential to fully assess its long-term effects, safety profile, and overall effectiveness in comparison to established treatment modalities. The technology and equipment needed for delivering Flash-RT are often expensive, which can limit accessibility for certain patients and healthcare facilities, potentially creating disparities in available treatment options. Currently, Flash-RT is primarily available in select clinical trial settings, which restricts access for many patients. This limited availability can hinder widespread adoption and implementation in routine clinical practice.
The operation of the specialized equipment used for Flash-RT requires highly trained personnel. The need for such expertise can pose challenges for facilities looking to incorporate this innovative treatment into their offerings.
What Are the Risks or Complications of Flash Radiotherapy?
While Flash radiotherapy (Flash-RT) presents promising advantages in cancer treatment, it is important to consider potential risks and complications associated with this innovative approach. As a relatively new and experimental treatment modality, Flash-RT carries certain uncertainties and challenges.
Given that Flash-RT is an emerging technology, the long-term consequences of exposure to ultra-high dose rates of radiation are not yet fully understood. Ongoing studies are necessary to assess potential late-onset side effects or complications that may arise after treatment, such as secondary cancers or long-term damage to healthy tissues.
Many ongoing clinical trials are still collecting data, which means that current findings may not provide a complete picture of the treatment’s efficacy and safety. Early trial results, while promising, may not capture all possible complications, necessitating further investigation to ensure that the treatment is both safe and effective for a diverse patient population.
The implementation of Flash-RT requires advanced technological capabilities and highly trained personnel to operate the specialized equipment effectively. Limited availability of such resources can lead to disparities in treatment access, potentially excluding patients who would benefit from this novel approach.

Learn More About Side Effectsof Conventional Radiotherapy: Special Article by OncoDaily
What Types of Cancer Are Treated with Flash Radiotherapy?
Flash radiotherapy (Flash-RT) is emerging as a novel treatment option for various cancer types, demonstrating promise in clinical trials. This innovative approach aims to deliver high doses of radiation in a very short time frame while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. Here are some of the key cancer types being studied and treated with Flash-RT:
Lung Cancer: Early trials indicate that Flash-RT can be effective for lung cancer treatment, with studies showing comparable or enhanced antitumor effects relative to traditional radiotherapy.
Pancreatic Cancer: Pancreatic cancer, known for its challenging treatment landscape, is being explored for Flash-RT applications.
Brain Tumors: Flash-RT is also being tested for treating brain tumors, where precision is crucial due to the delicate nature of brain tissues.
Solid Tumors: A significant focus of ongoing research is the application of Flash-RT in solid tumors across various anatomical sites.
Head and Neck Cancers: Given the high doses often required for effective treatment, Flash-RT is being considered for head and neck cancers.
Breast Cancer: Research into Flash-RT for breast cancer is also underway, with studies examining its potential to improve outcomes while reducing side effects related to traditional treatment modalities.
Gastrointestinal Cancers: Flash-RT is being explored in the context of gastrointestinal cancers, where the treatment often involves challenges related to radiation-induced damage to the surrounding organs.
How to Prepare for Flash Radiotherapy
Preparing for Flash Radiotherapy involves several important steps to ensure a smooth treatment experience. First, consult with your healthcare team to understand the specific details about your treatment plan, including the type of cancer being treated and the expected outcomes of Flash Radiotherapy. It’s essential to discuss any pre-existing health conditions or medications you are taking, as this information is crucial for your treatment planning.
Schedule any necessary imaging or tests prior to the treatment, such as CT scans or MRIs, to precisely locate the tumor and determine the optimal approach for your Flash-RT. Following any dietary guidelines provided by your healthcare team is important, as they may recommend specific dietary modifications leading up to the treatment to optimize your overall health.
Make arrangements for transportation to and from the treatment facility, as you may feel fatigued or unwell after your session. Prepare for potential side effects by discussing them with your healthcare team, understanding what to expect can help you manage any discomfort more effectively. Lastly, stay informed and ask questions about the procedure, including what will happen during the treatment session and any follow-up care required afterward.
Medical Consultation
A comprehensive consultation with the oncologist or radiotherapy specialist is crucial for several reasons. This initial meeting serves as an opportunity to delve deeply into your medical history, allowing the healthcare team to assess any pre-existing conditions or treatments that may influence the approach to Flash Radiotherapy. Understanding the patient’s unique health profile is essential for tailoring an effective and safe treatment plan.
During this consultation, the treatment plan will be thoroughly discussed, outlining the objectives of Flash Radiotherapy and how it differs from traditional methods. This includes explaining the rationale behind the use of ultra-high dose rates and the potential benefits it offers in terms of tumor control and reduced damage to healthy tissues.
It’s equally important to address any potential risks or side effects associated with the treatment. Engaging in an open dialogue about these concerns ensures that patients are well-informed and can make educated decisions regarding their care. The discussion may cover aspects such as the likelihood of experiencing common side effects like fatigue, skin irritation, or nausea, as well as strategies for managing these issues effectively.
Furthermore, this consultation is an ideal time for patients to voice any questions or concerns they might have about the procedure, expected outcomes, and the overall treatment experience. Whether it’s clarifying details about the treatment process, discussing the duration of sessions, or understanding the follow-up care required, having a thorough and transparent conversation can alleviate anxieties and empower patients in their cancer journey.
Imaging and Planning
In preparation for Flash Radiotherapy, patients typically undergo a series of imaging scans, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This imaging process is essential for accurately mapping the tumor’s location and size, a phase often referred to as “simulation.”
During this phase, advanced imaging techniques provide detailed visualizations of the tumor and the surrounding anatomical structures. These scans play a critical role in treatment planning by identifying the tumor’s exact location within the body, assessing its size to customize the radiation dose and technique, and ensuring precise targeting. Accurate imaging allows the radiation oncologist to determine the most effective angles and positions for delivering radiation, which is especially important in Flash Radiotherapy.
Pre-Treatment Guidelines
Before undergoing Flash Radiotherapy, patients should adhere to specific pre-treatment guidelines to ensure the best possible outcomes and minimize any potential risks. Depending on the specifics of the treatment plan and consultation with the healthcare team, patients may be advised to fast for a certain period before their session. This is particularly relevant if sedation or anesthesia is involved. Patients should clarify any dietary restrictions with their medical team in advance. Patients may need to avoid certain medications before the treatment. This can include blood thinners or any drugs that could interfere with the radiotherapy process. It’s crucial to review all current medications with the oncologist to make necessary adjustments.
Maintaining the skin in the treatment area is important. Patients should be advised to avoid applying lotions, creams, or perfumes on the skin where radiation will be administered. This helps prevent irritation and ensures that the radiation can penetrate effectively. Staying calm and relaxed before treatment is vital. Stress and anxiety can negatively affect a patient’s overall experience and response to treatment. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or engaging in calming activities can be beneficial in creating a positive mindset.
Immobilization Devices
In Flash Radiotherapy, the use of immobilization devices is crucial to ensure that patients remain in a consistent position throughout the treatment session. This precision is vital for maximizing the effectiveness of the radiation while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
Types of Immobilization Devices: Various types of immobilization devices or masks may be employed, depending on the treatment area and patient needs. These can include custom molds, thermoplastic masks, or cushions designed to securely hold the patient in place during the procedure.
Fitting Process: The fitting of these devices is typically performed during the simulation phase, where imaging scans are taken to identify the tumor’s exact location and size. During this fitting, patients may be asked to lie in the treatment position for a brief period while the device is molded or adjusted to their body shape. This process ensures that the device aligns precisely with the anatomical features of the patient, allowing for accurate targeting during treatment.
Importance of Precision: Maintaining a consistent position is essential in Flash Radiotherapy due to the ultra-high dose rates used in treatment. Even slight movements can lead to inaccuracies in targeting the tumor, potentially affecting treatment efficacy and increasing the risk of damage to healthy tissues. Immobilization devices help mitigate these risks by stabilizing the patient, allowing for focused delivery of radiation to the intended area.
The incorporation of immobilization devices into the treatment plan is a critical step in enhancing the precision and safety of Flash Radiotherapy. Patients can feel assured that these measures are in place to provide the most effective treatment possible while prioritizing their overall health and well-being.
Mental and Emotional Preparation
Mental and emotional preparation plays a vital role in ensuring a positive experience for patients undergoing Flash Radiotherapy. The anticipation of treatment can often lead to feelings of anxiety and stress, therefore, implementing strategies to manage these emotions is essential.
Engaging in relaxation methods can significantly alleviate pre-treatment anxiety. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises help calm the mind and body by promoting relaxation. Simple practices like inhaling deeply through the nose and exhaling slowly through the mouth can ground patients in the moment and reduce tension. Incorporating meditation into daily routines can enhance emotional well-being. Mindfulness practices encourage individuals to focus on the present moment, reducing worry about the treatment process. Guided meditation apps or videos can provide structured sessions to help patients navigate their emotions. Building a strong support network is invaluable during this time. Reaching out to friends, family, or support groups allows patients to express their feelings and receive encouragement. Professional support from therapists or counselors specializing in oncology can also provide coping strategies tailored to individual needs.
One of the advantages of Flash Radiotherapy is its significantly shorter treatment sessions compared to traditional radiotherapy methods. These brief appointments not only minimize the time spent in a clinical environment but also reduce the associated stress that longer sessions may provoke. Knowing that the treatment is quick can provide reassurance and contribute to a more relaxed mindset.
Post-Treatment Care Expectations
Therapy is designed to be faster and less demanding on the body, recovery and observation remain critical. Patients are often encouraged to rest after their sessions, as the body may need time to recover from radiation exposure. Resting helps restore energy and composure.
Healthcare providers monitor patients closely for any immediate side effects, even though Flash Radiotherapy aims to reduce toxicity. Fatigue, skin irritation, or nausea may still occur, and identifying these side effects early ensures they are promptly managed. Regular follow-up appointments are an integral part of the recovery process, allowing medical teams to evaluate the patient’s progress, address any ongoing effects, and adjust care plans as needed.
Recovery is emphasized throughout the post-treatment phase, with patients advised to prioritize self-care and adhere to any guidelines provided by their healthcare team. Recommendations may include maintaining proper hydration, following a nutritious diet, and managing activity levels. Although Flash Radiotherapy offers advantages in speed and efficiency, thorough observation and care are vital for achieving the best possible outcomes and supporting patients throughout their recovery journey.

Know Your Doctor: Learn More About Who is Radiation Oncologist: Special Article by OncoDaily
What Are the Signs Flash Radiotherapy is Working?
The effectiveness of Flash Radiotherapy is assessed through various indicators and methods over time, providing insights into how well the treatment is achieving its intended outcomes. Here’s an overview of how the success of Flash Radiotherapy is evaluated:
Imaging Studies: Regular imaging studies, such as CT or MRI scans, play a crucial role in monitoring the response to treatment. These scans allow healthcare providers to observe changes in tumor size or structure, helping to determine if the tumor is responding positively to the high-dose radiation.
Symptom Relief: Patients often report changes in their symptoms as a key measure of treatment effectiveness. A reduction in symptoms associated with cancer, such as pain or discomfort, can be a strong indicator that Flash Radiotherapy is working. Tracking these changes is essential for evaluating patient progress.
Tumor Markers: In some cases, specific tumor markers may be used to assess the effectiveness of treatment. These biomarkers can provide valuable information regarding the presence of cancer cells in the body. A decrease in these markers after treatment can signal a successful response to Flash Radiotherapy.
Follow-Up Appointments: Scheduled follow-up appointments are vital for ongoing assessment. During these visits, healthcare providers review patient history, conduct physical examinations, and discuss any side effects or changes in health. This comprehensive evaluation helps in understanding the treatment’s impact over time.
Patient Feedback: Collecting feedback from patients regarding their overall health and well-being is also an important part of measuring the effectiveness of Flash Radiotherapy. Patient-reported outcomes, including quality of life assessments, can provide insights into how the treatment is affecting their daily lives and overall health.
Long-Term Monitoring: Given that Flash Radiotherapy is still an emerging treatment, long-term monitoring is crucial for understanding its full impact. Researchers and healthcare providers continue to study patients over extended periods to evaluate the durability of responses and any potential late effects of treatment.
By employing a combination of these methods, healthcare teams can effectively gauge the success of Flash Radiotherapy, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment plans if necessary and ensuring that patients receive the best possible care throughout their cancer journey.
Imaging and Tumor Response
Imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans are commonly used to visualize the tumor’s size, structure, and any changes that occur after treatment. These methods are essential for assessing whether the tumor has shrunk or stabilized following Flash Radiotherapy, with comparisons of pre- and post-treatment images providing a clear measure of the therapy’s impact. One distinct advantage of Flash Radiotherapy is the potential for its effects to be observed more quickly than with traditional radiation methods, allowing for faster evaluations of treatment efficacy. Continuous imaging also supports real-time monitoring of the tumor’s response, enabling adjustments to the treatment plan when needed. This dynamic use of imaging provides valuable insights into the performance of Flash Radiotherapy, offering a more timely and accurate understanding of patient outcomes.
Symptom Relief
Relief from symptoms may include a reduction in pain, swelling, and other cancer-related issues. For example, patients with tumors exerting pressure on surrounding tissues might experience less discomfort. The location of the tumor can affect how quickly symptoms improve, with those having superficial tumors often noticing relief sooner than patients with deeper or more complex tumors. Many individuals begin to feel symptom relief within a few days to a couple of weeks after treatment, which is one of the advantages of the high-dose rates used in Flash Radiotherapy. Regular follow-up appointments and assessments remain essential to monitor symptom progression and adjust treatment as needed, ensuring continuous support. Overall, Flash Radiotherapy often leads to earlier improvements in symptoms compared to traditional treatments, enhancing the quality of life for patients.
Biomarkers and Clinical Follow-Up
Monitoring biomarkers and conducting regular follow-up appointments are vital for evaluating the effectiveness of Flash Radiotherapy. Blood tests play a key role by identifying specific biomarkers linked to tumor activity, allowing healthcare providers to determine if the treatment is successfully reducing the tumor burden and if the cancer is responding positively. Alongside biomarker analysis, clinical signs such as symptom changes, physical examination findings, and imaging results are assessed to provide a clearer picture of the patient’s response to therapy. Regular follow-up visits are essential for tracking progress, managing side effects, and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Combining biomarker monitoring with clinical evaluations gives a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s response, enabling timely interventions and ensuring the best possible care throughout their treatment journey.
Innovations in Flash Radiotherapy
Recent advancements in Flash Radiotherapy are transforming cancer treatment by emphasizing precision and efficiency. Artificial intelligence is playing a pivotal role in enhancing the accuracy of tumor targeting, with AI systems analyzing large datasets to refine treatment plans and optimize dose delivery. This approach minimizes the impact on healthy tissues while maximizing the therapeutic effects on cancer cells. Additionally, specialized equipment designed specifically for delivering Flash doses has been developed, capable of achieving the ultra-high dose rates required for this innovative therapy. Ongoing clinical trials are also exploring the safety and efficacy of Flash Radiotherapy across various types of cancer, providing essential data to guide its future applications. These developments underscore the potential of Flash Radiotherapy to reshape cancer care and improve patient outcomes.
Bourhis et al. treated a 75-year-old patient with advanced skin lymphoma using a single FLASH radiotherapy dose (15 Gy in 90 ms). Side effects were mild (skin redness and slight swelling), and the tumor showed a rapid and lasting response over five months. These findings point to the potential of FLASH-RT for effective tumor control with reduced harm to normal skin, but further studies are needed.
What Happens After Flash Radiotherapy?
Regular follow-up visits with your oncologist or radiotherapy team are essential for monitoring recovery, managing side effects, and adjusting your care plan as needed. Common side effects include fatigue and skin reactions like redness or irritation, which usually lessen over time. To support your recovery, prioritize rest, engage in light physical activity, and maintain a balanced diet. For skin care, use gentle cleansers, moisturize the treated area, and avoid sun exposure as advised by your healthcare team.
Stay vigilant for any signs of cancer recurrence by being aware of new symptoms and communicating any concerns with your medical team. Additionally, seeking emotional and psychological support from friends, family, or support groups can greatly aid in coping with stress and anxiety during your treatment journey.
How Much Does Flash Radiotherapy Cost?
Flash Radiotherapy (Flash-RT) uses specialized, high-cost equipment to deliver high-dose radiation in fewer sessions, which can still lead to significant overall treatment expenses. Patients may also incur additional costs for consultations, imaging, and follow-up appointments. Since Flash-RT is experimental, insurance coverage might be limited, but participating in clinical trials can offer free treatment. Additionally, various financial assistance programs, including grants and support from healthcare facilities, are available to help reduce the financial burden.
Recovery of the Body After Flash Radiotherapy
The recovery process following Flash Radiotherapy tends to be more efficient compared to traditional radiation treatments due to the technology’s design to minimize damage to healthy tissues. This reduction in collateral damage can lead to quicker recovery times and an overall improved quality of life for patients.
- Faster Recovery: Patients often report feeling less fatigued and experience fewer side effects, which facilitates a smoother transition back to normal activities. Early trial data suggest that many individuals resume their daily routines more swiftly after Flash-RT compared to conventional therapies.
- Post-Treatment Care: Effective post-treatment care is crucial for optimal recovery. Patients are advised to:
- Rest and Hydrate: Ensuring adequate rest and hydration is essential for the body to heal effectively.
- Manage Side Effects: While side effects are typically less severe, some patients may still experience mild skin irritation or fatigue. Monitoring these symptoms and addressing them promptly is important.
- Mental Health Support: Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as mindfulness or gentle yoga, can help manage anxiety and improve overall well-being. Support from friends, family, or professional counseling may also be beneficial during the recovery phase.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Incorporating a balanced diet and light exercise can aid in physical recovery. Patients are encouraged to listen to their bodies and gradually increase activity levels as tolerated.
If You Want To Stay Updated From Latest Radiation Oncology Research You can Read Special Articles by Oncodaily on Major Radiation Oncology Conferances: ASTRO and ESTRO
Written by Aren Karapetyan, MD
FAQ
How long does a typical Flash Radiotherapy session last?
A typical Flash Radiotherapy session lasts only a few minutes, as the treatment delivers a very high dose of radiation in a fraction of a second.
Can Flash Radiotherapy be combined with other treatments?
Yes, Flash Radiotherapy can be combined with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy, to enhance its effectiveness.
Does Flash Radiotherapy hurt?
Reassure patients that Flash-RT itself is painless. However, discuss potential side effects that may develop post-treatment, such as skin irritation or fatigue. Offer tips on managing discomfort and advice on when to consult a healthcare provider.
How is Flash Radiotherapy monitored during treatment?
During Flash Radiotherapy, advanced imaging and monitoring technologies are employed to ensure precise targeting of the tumor. Continuous imaging may be used to verify the tumor's position and size in real-time, allowing for adjustments if necessary. These systems help minimize the risk of radiation exposure to surrounding healthy tissues, ensuring effective treatment delivery.
Can patients eat before a Flash Radiotherapy session?
Whether patients can eat before a Flash Radiotherapy session depends on the specific instructions given by their medical team. In some cases, patients may need to fast for a few hours prior to treatment to ensure optimal conditions. It is crucial for patients to follow the guidance of their healthcare provider regarding dietary restrictions to avoid any complications.
What should patients expect during their first Flash Radiotherapy session?
During their first Flash Radiotherapy session, patients can expect a thorough explanation of the procedure by their healthcare team. Initial preparations will involve imaging scans to determine the exact treatment area and fitting for any necessary immobilization devices. Once in the treatment room, the procedure will be conducted swiftly, often lasting only a few seconds, with continuous monitoring to ensure safety and accuracy.
Are there specific side effects to watch for after Flash Radiotherapy?
After undergoing Flash Radiotherapy, patients should be aware of potential side effects, including skin reactions, fatigue, and localized swelling. Monitoring for these symptoms is essential, as they may vary in intensity and duration. Patients are encouraged to keep track of any changes and report significant or concerning symptoms to their healthcare provider for proper management.
How does Flash Radiotherapy impact daily life after treatment?
Flash Radiotherapy may allow for a quicker return to daily activities compared to traditional treatments, as it typically results in less damage to healthy tissues. Many patients report feeling well enough to resume normal routines sooner. However, it is essential to listen to one’s body and gradually increase activity levels, taking time to rest and recover as needed.
Is there ongoing research into the long-term effects of Flash Radiotherapy?
Yes, there is ongoing research focused on understanding the long-term effects of Flash Radiotherapy. Clinical trials are investigating various aspects, including treatment outcomes, potential late effects, and the long-term health of patients who have undergone Flash-RT. These studies aim to ensure the safety and effectiveness of this innovative approach in oncology.


