The CodeBreaK 300 trial, a phase III randomized study, evaluated the efficacy of combining sotorasib, a KRAS G12C inhibitor, with panitumumab, an anti-EGFR antibody, in patients with chemorefractory metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) harboring the KRAS G12C mutation. This mutation, present in approximately 3%–4% of mCRC cases, is associated with poor prognosis and limited treatment options. The study compared two dosing regimens of sotorasib (960 mg and 240 mg daily) plus panitumumab against standard-of-care treatments (trifluridine/tipiracil or regorafenib).
The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS), with overall survival (OS) as a key secondary endpoint. The trial demonstrated that the combination of sotorasib 960 mg with panitumumab significantly improved PFS compared to standard therapies, suggesting a potential new treatment avenue for this patient population.
Title: Overall Survival Analysis of the Phase III CodeBreaK 300 Study of Sotorasib Plus Panitumumab Versus Investigator’s Choice in Chemorefractory KRAS G12C Colorectal Cancer
Authors: Filippo Pietrantonio, MD, Lisa Salvatore, MD, Taito Esaki, MD, Dominik Paul Modest, MD, David Paez Lopez-Bravo, MD, Julien Taieb, MD, Michalis V. Karamouzis, MD, Erika Ruiz-Garcia, MD, Tae Won Kim, MD, Yasutoshi Kuboki, MD,Fausto Meriggi, MD, David Cunningham, MD, Kun-Huei Yeh, MD, PhD, Emily Chan, MD, PhD, Joseph Chao, MD, Qui Tran, PhD, Chiara Cremolini, MD, Marwan Fakih, MD
Published in JCO Oncology, April 2025
Background
Colorectal cancer (CRC) harboring KRAS G12C mutations accounts for approximately 3%–4% of cases and is associated with poor clinical outcomes and limited treatment options. Sotorasib, a targeted inhibitor of KRAS G12C, has emerged as a promising therapy for this subset of patients. The CodeBreaK 300 trial was designed to assess the efficacy and safety of combining sotorasib with panitumumab, an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody, versus standard-of-care (SOC) treatments in previously treated patients with KRAS G12C–mutated metastatic CRC.
Methods
This randomized, open-label, phase III trial enrolled patients with KRAS G12C–mutated metastatic CRC who had received prior standard therapies. Participants were randomized to receive either sotorasib plus panitumumab or SOC treatments, which included trifluridine-tipiracil or regorafenib. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS), with overall survival (OS) as a key secondary endpoint.
Study Design
Patients with KRAS G12C–mutated metastatic CRC, previously treated with standard therapies were included.
- Intervention: Sotorasib (960 mg orally once daily) plus panitumumab (6 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks).
- Comparator: SOC treatments (trifluridine-tipiracil or regorafenib).
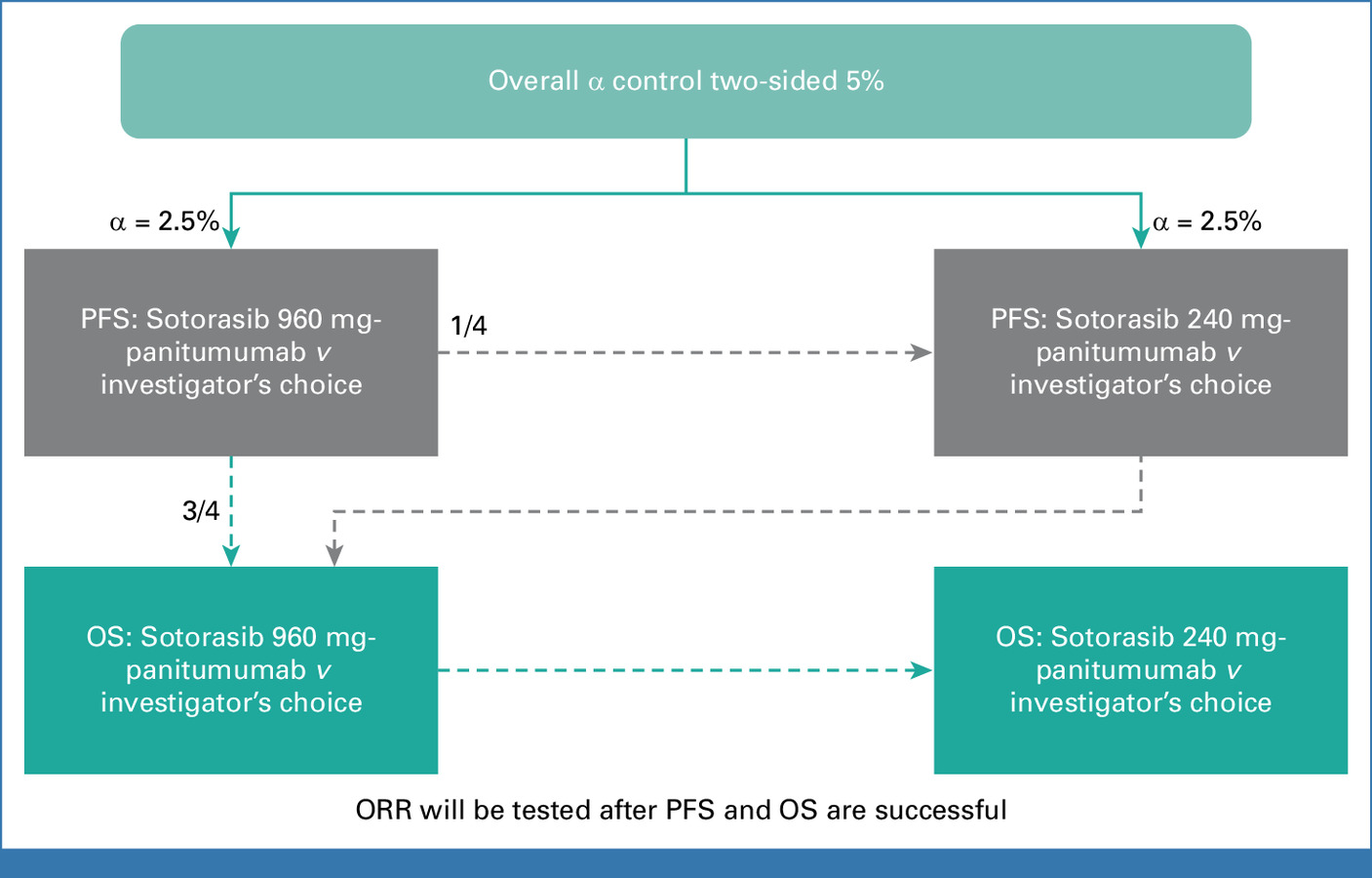
Endpoints:
- Primary: Progression-free survival (PFS).
- Secondary: Overall survival (OS), objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and safety.
Results
The CodeBreaK 300 study demonstrates that sotorasib combined with panitumumab provides a significant clinical benefit over standard therapies in patients with KRAS G12C–mutated metastatic CRC, particularly in terms of PFS and ORR. The manageable safety profile supports the consideration of this combination as a new treatment option for this patient population.
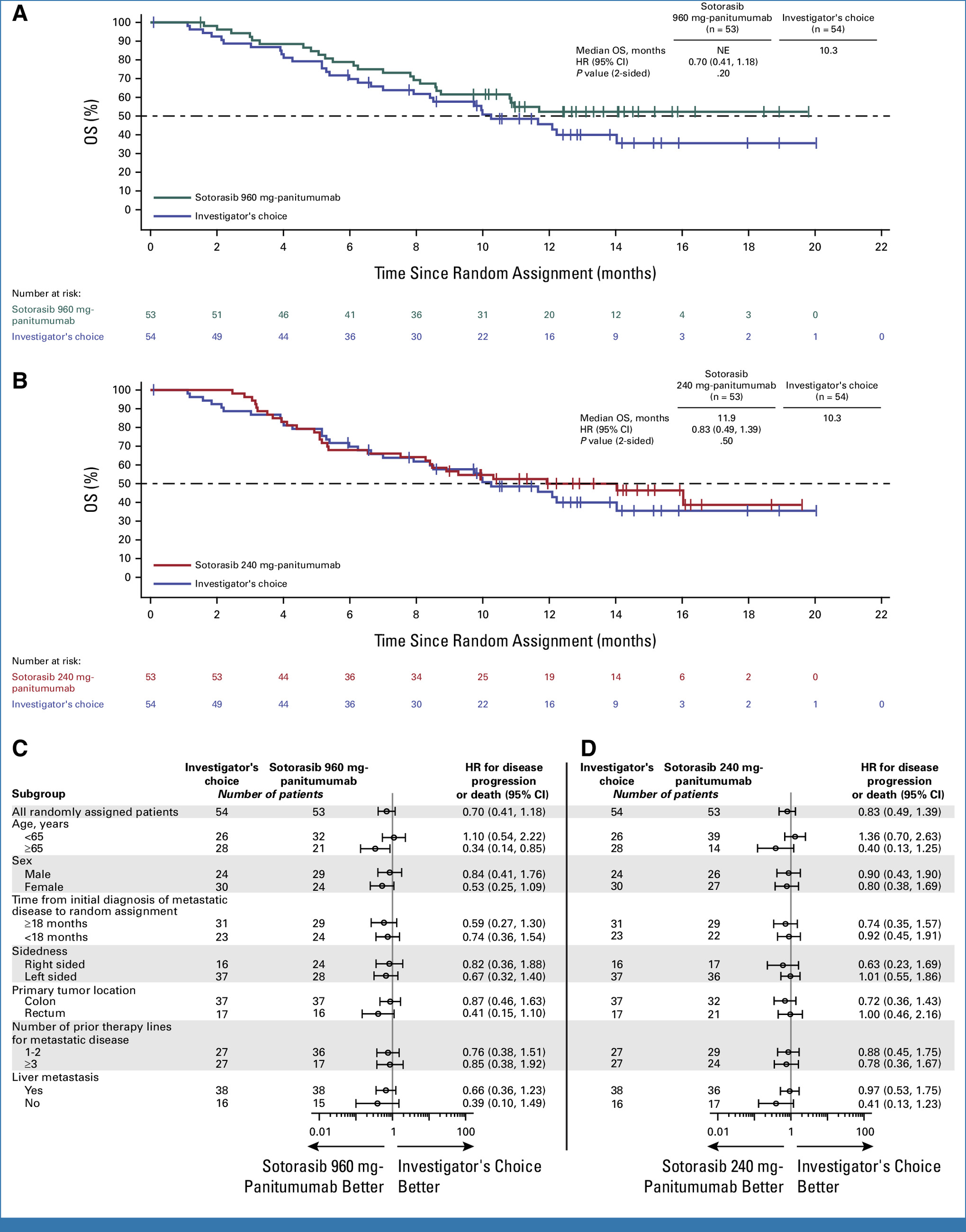
- At a median follow-up of 13.6 months
- Median OS was 14.1 months in the sotorasib plus panitumumab group versus 11.5 months in the SOC group.
- Hazard ratio (HR) for death was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.53 to 1.11).
- Median PFS was 5.6 months with sotorasib plus panitumumab compared to 2.2 months with SOC.
- HR for disease progression or death was 0.49 (95% CI, 0.34 to 0.71).
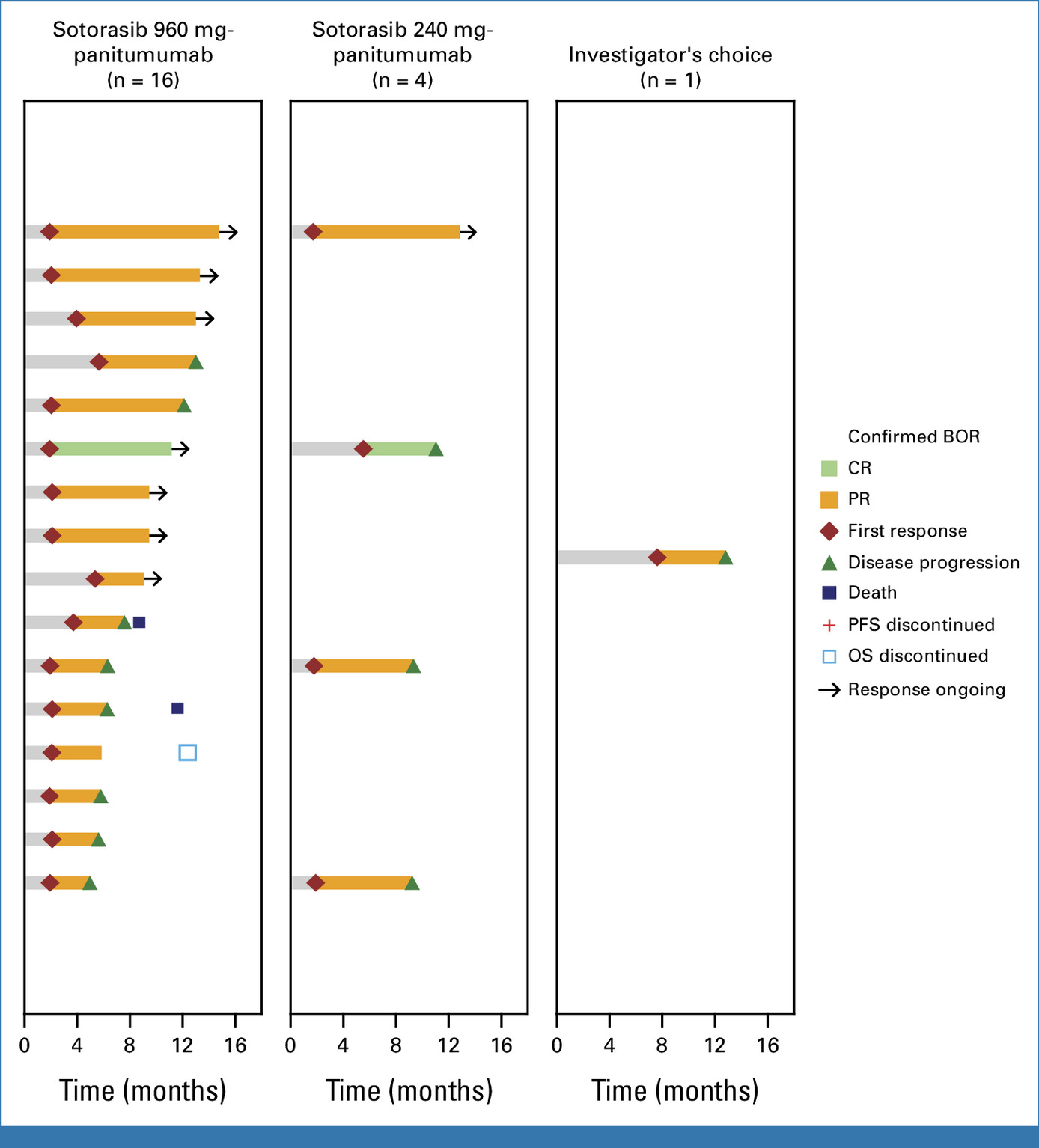
- ORR was 26% in the combination therapy group versus 2% in the SOC group.
- DCR was 81% with sotorasib plus panitumumab compared to 33% with SOC.
- Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 34% of patients in the combination group and 31% in the SOC group.
Key Findings
- The combination of sotorasib and panitumumab significantly improved PFS and ORR compared to SOC in patients with KRAS G12C–mutated metastatic CRC.
- While the improvement in OS did not reach statistical significance, a positive trend was observed.
- The safety profile of the combination therapy was manageable and consistent with known profiles of the individual agents.
Key Takeaway Messages
- Targeting KRAS G12C mutations with sotorasib in combination with panitumumab offers a promising treatment strategy for a subset of metastatic CRC patients with limited options.
- The significant improvements in PFS and ORR highlight the potential clinical benefit of this combination therapy.
- Further research is warranted to confirm the OS benefit and to explore the combination in earlier lines of therapy.
You can read the full article here
Written by Sona Karamyan, MD


