
New Paper Alert: KRAS-Targeted Therapies in Colorectal Cancer: Promising Therapies for KRAS G12D and G12V in CRC
KRAS G12D and G12V mutations are among the most frequent alterations in colorectal cancer (CRC), collectively accounting for a substantial portion of all KRAS-mutant cases. These mutations are associated with tumor aggressiveness and resistance to conventional therapies, posing significant challenges in clinical management. However, recent advances in molecular oncology have driven the development of targeted treatments, including small-molecule inhibitors, T-cell receptor (TCR) therapies, and mRNA vaccines specifically designed to address these variants. As research progresses, these strategies hold promise to transform outcomes for patients with KRAS G12D and G12V-mutated CRC, ushering in a new era of precision therapy.
Title: Ready, Set, Go: Setting Off on the Mission to Target KRAS in Colorectal Cancer
Authors: Andrew J. Pellatt, MD, Deepak Bhamidipati, MD, Vivek Subbiah, MD
Published in JCO, April 2025
Background
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Mutations in the KRAS gene are present in approximately 40% of CRC cases, with specific variants such as G12D and G12V being particularly prevalent. These mutations contribute to tumor progression and have historically been challenging to target therapeutically. Recent advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have opened new avenues for treating KRAS-mutant CRC.
Methods
The article reviews current strategies aimed at targeting KRAS mutations in CRC, focusing on the development and evaluation of various therapeutic approaches. It synthesizes data from preclinical studies and clinical trials to assess the efficacy of small-molecule inhibitors, proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs), T-cell receptor (TCR) therapies, and vaccines specifically designed to target KRAS G12D and G12V mutations.
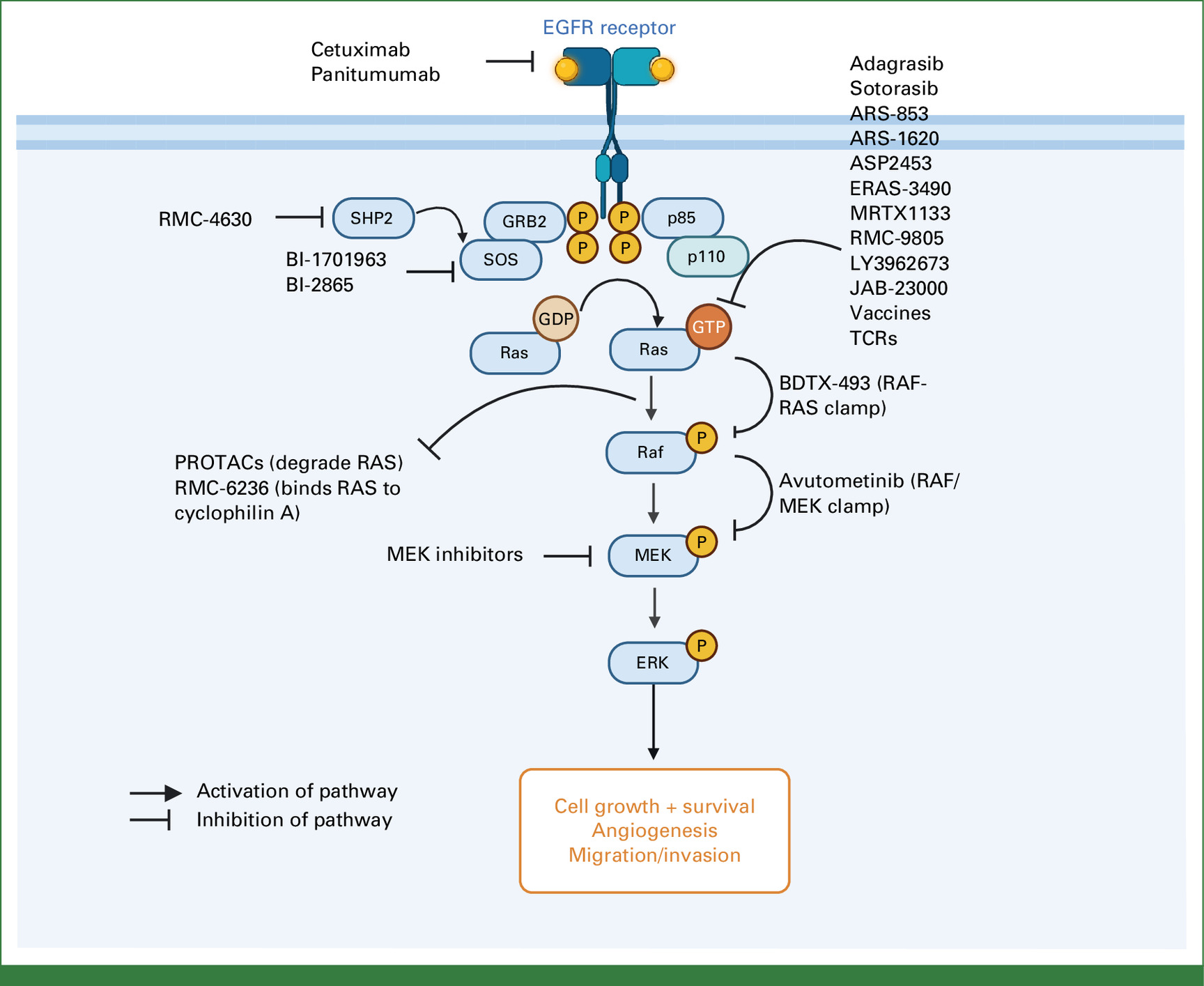
Study Design
This comprehensive review analyzes existing literature on KRAS-targeted therapies in CRC. It evaluates the biological rationale for different treatment strategies, including monotherapies and combination therapies, and considers the mechanisms of resistance that may arise with these treatments.
Results
The pursuit of effective treatments for KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer, particularly those harboring G12D and G12V mutations, has led to significant advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies. While challenges remain, the development of small-molecule inhibitors, combination strategies, and innovative immunotherapies offers hope for improved patient outcomes. Ongoing clinical trials and further research are crucial to validate these approaches and integrate them into standard treatment protocols.
- KRAS G12D and G12V Mutations: These specific mutations are among the most common in CRC, with G12D present in approximately 30%–36% of cases and G12V in a significant proportion as well. Targeting these mutations has been a focus of recent research efforts.
- Small-Molecule Inhibitors: The development of inhibitors like MRTX1133, which targets KRAS G12D, has shown promise in preclinical models. Studies have demonstrated strong synergy between MRTX1133 and chemotherapy agents such as 5-FU in pancreatic and colon cancer models, indicating potential for enhanced efficacy at lower doses.
- Combination Therapies: Combining KRAS inhibitors with other targeted agents, such as EGFR inhibitors, has been explored to enhance treatment responses and mitigate resistance. For example, combining KRAS G12C inhibitors with EGFR inhibitors has shown improved efficacy in CRC patients.
- Immunotherapies and Vaccines: Innovative approaches, including mRNA vaccines like mRNA-5671/V941, have been developed to target multiple KRAS mutations, including G12D and G12V. These vaccines aim to elicit an immune response against KRAS-mutant tumor cells. However, clinical development has faced challenges, and further research is needed to establish their efficacy.
- Clinical Trials and Outcomes: Multiple early-phase clinical trials are underway to evaluate TCR therapies targeting KRAS G12V mutations, such as NCT0610521 and NCT06043713. These trials aim to assess the safety and efficacy of novel TCR-based treatments in CRC patients.
Key Findings
- Prevalence of KRAS Mutations: KRAS mutations, particularly G12D and G12V, are highly prevalent in CRC, necessitating targeted therapeutic strategies.
- Advancements in Targeted Therapies: The development of small-molecule inhibitors and combination therapies has shown potential in preclinical and early clinical studies, offering new hope for patients with KRAS-mutant CRC.
- Emerging Immunotherapies: Innovative approaches, including TCR therapies and mRNA vaccines, are being explored to target KRAS mutations, though their clinical efficacy remains under investigation.
Key Takeaway Messages
- Targeting KRAS G12D and G12V mutations in CRC is a critical area of ongoing research, with several therapeutic strategies showing promise in preclinical and early clinical settings.
- Combination therapies that include KRAS inhibitors and other targeted agents may enhance treatment efficacy and overcome resistance mechanisms.
- Continued clinical trials are essential to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of these novel therapies and to translate preclinical findings into clinical practice.
American You can read the full article here
Written by Sona Karamyan, MD
-
Challenging the Status Quo in Colorectal Cancer 2024
December 6-8, 2024
-
ESMO 2024 Congress
September 13-17, 2024
-
ASCO Annual Meeting
May 30 - June 4, 2024
-
Yvonne Award 2024
May 31, 2024
-
OncoThon 2024, Online
Feb. 15, 2024
-
Global Summit on War & Cancer 2023, Online
Dec. 14-16, 2023
