María Natalia Gandur Quiroga, Medical Oncologist and Chief of the Division of Genitourinary Medical Oncology at the Ángel H. Roffo Oncology Institute, shared a post about recent article by Claudia Galassi et al. on X:
“Amazing article. Must read.
Hallmarks of Cancer Immune Evasion.
Exploring the ‘Three Cs’ Conceptual Framework
General Overview
The immune system can eliminate or control malignant cells, preventing their proliferation until they acquire genetic or epigenetic alterations that allow immune escape.
Immune evasion enables tumors to resist not only immune detection but also targeted therapies and immunotherapies.
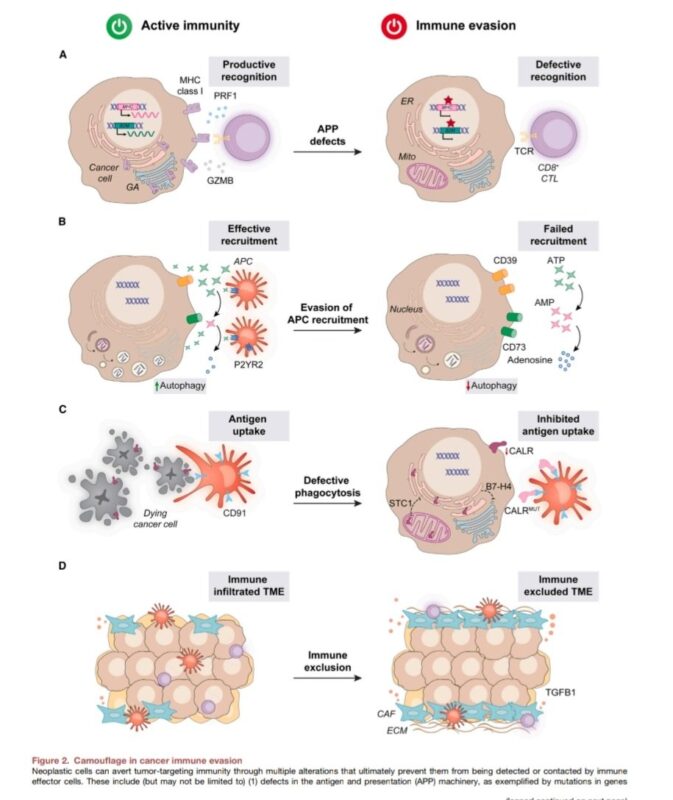
1. Camouflage: Strategies for cancer cells to avoid detection or recognition as malignant.
– Antigen Processing and Presentation (APP) Defects: Mutations in MHC or B2M genes decrease the visibility of cancer cells to cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
– Reduced Secretion of Chemotactic Factors: Limits the attraction of antigen-presenting cells (APCs), creating a barrier to immune infiltration.
– Physical Exclusion: Formation of collagen-rich, stromal barriers (e.g., cancer-associated fibroblasts) that block immune cell entry.
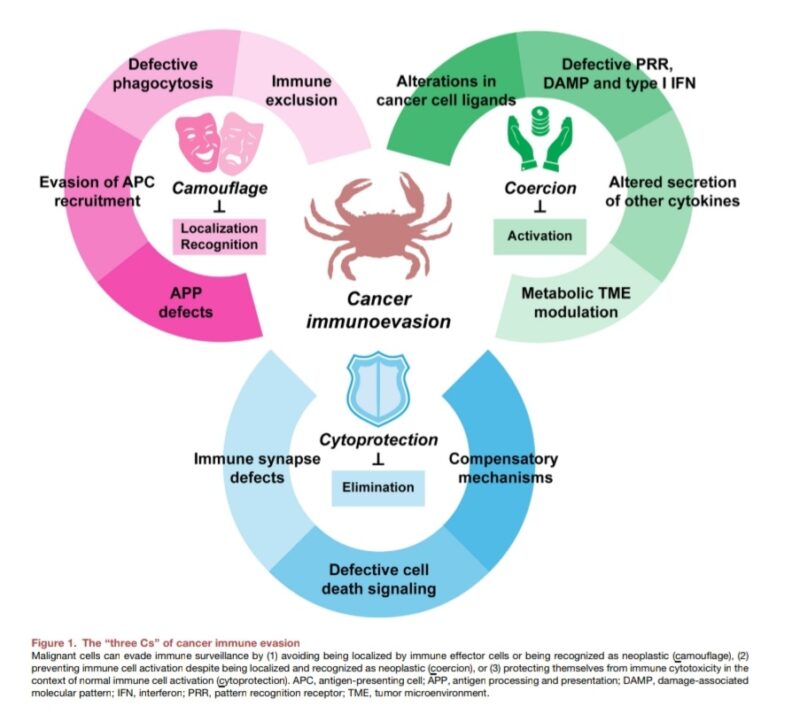
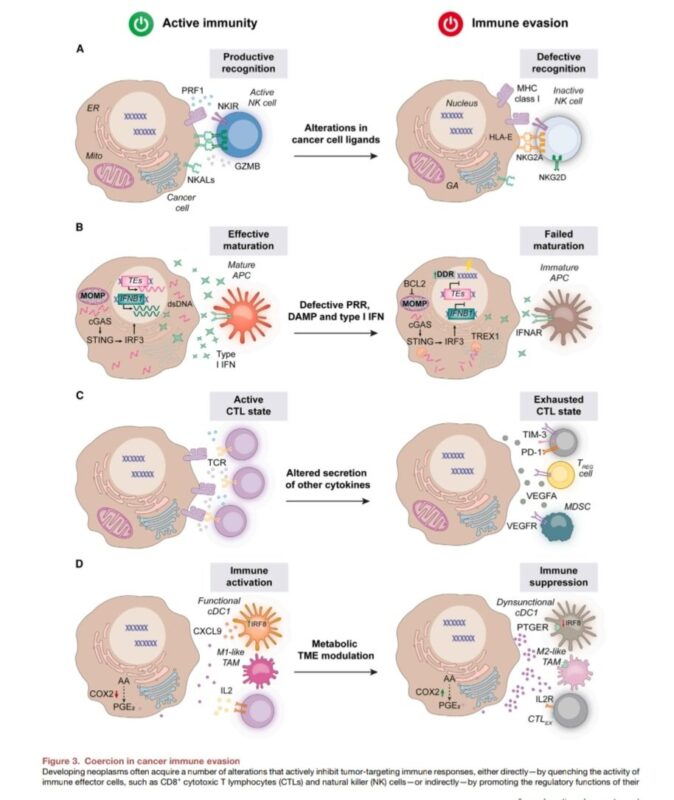
2. Coercion: Direct or indirect suppression of immune effector cell activity.
– PD-L1 and Other Immunomodulatory Ligands: Malignant cells upregulate PD-L1 to inhibit T cells and NK cells.
– Epigenetic Modifications and NK Cell Ligands: Reduced NK cell-activating ligands allow cancer cells to evade NK cell cytotoxicity.
– Disruption of DAMP and Type I IFN Signaling: Alterations in molecules like CGAS-STING lower pro-inflammatory immune responses in the tumor microenvironment.
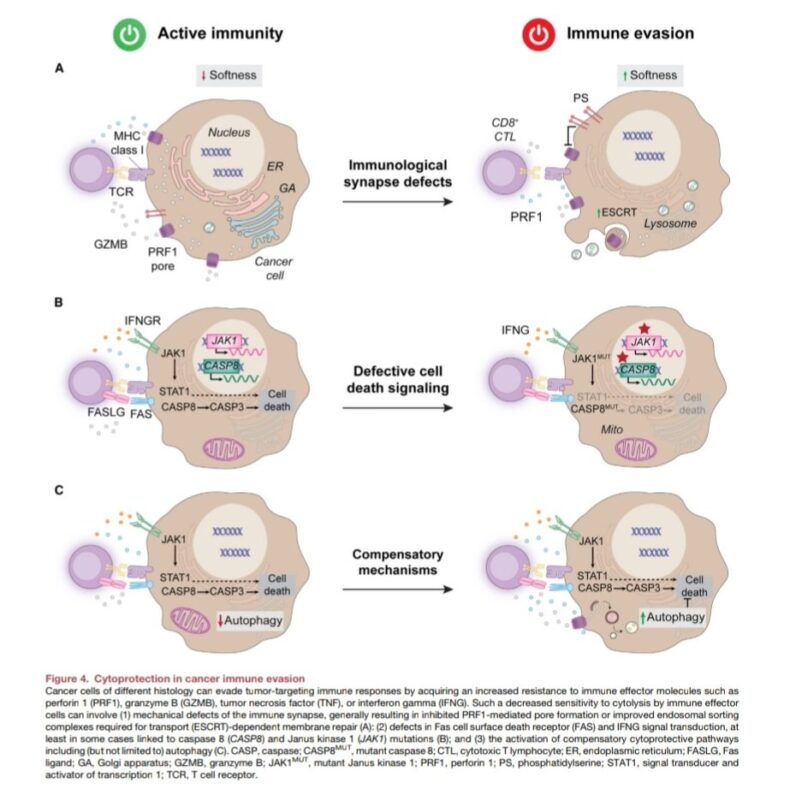
3. Cytoprotection: Mechanisms that shield malignant cells from immune cytotoxicity.
– Protection from Immune-Induced Cell Death: Molecular and physical barriers protect cancer cells from cytotoxic immune activity.
– Anti-Phagocytic Proteins (like CD47): Cancer cells express proteins that prevent phagocytosis by APCs.
– Metabolic Alterations: Metabolic shifts, such as increased lactate secretion and hypoxia, suppress immune cell function in the tumor microenvironment.
Therapeutic Implications
Therapeutic approaches need to address these immune evasion mechanisms beyond simply activating antitumor immunity.
Targeting the ‘Three Cs’ offers a novel framework to combine with conventional immunotherapies, enhancing efficacy and promoting an effective immune response.
By framing immune evasion through the ‘Three Cs,’ this perspective redefines how we understand and approach cancer immune resistance, creating new opportunities for therapeutic strategies.”
The hallmarks of cancer immune evasion
Authors: Claudia Galassi, Timothy A. Chan, Ilio Vitale, Lorenzo Galluzzi

More posts about María Natalia Gandur Quiroga.
María Natalia Gandur Quiroga is a Medical Oncologist and Chief of the Division of Genitourinary Medical Oncology at the Ángel H. Roffo Oncology Institute in Buenos Aires, Argentina. She is a Professor of Medicine at the University of Buenos Aires at the Oncologists Post Graduates Studies.
Her research focuses on clinical trials with aims to improve the treatment of patients with urologic tumors. She is an active member of the European Association for Cancer Research, Argentinian Medical Association and American Society of Clinical Oncology.
