John Gordon, VP Scientific Affairs, Co-Founder and Director at Celentyx Ltd, shared an article by Robin Reschke on LinkedIn:
“Immunotherapy | Immune Related Adverse Events | Targeting Molecular Pathways to Control Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicities | Breaking Review from Robin Reschke et al at Trends in Immunology Cell Press.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have transformed cancer treatment but are frequently associated with immune-related adverse events (irAEs). This article offers a novel synthesis of findings from both preclinical and clinical studies, focusing on the molecular mechanisms driving irAEs across diverse organ systems.
It examines key immune cells, such as T cell subsets and myeloid cells, which are instrumental in irAE pathogenesis, alongside an in-depth analysis of cytokine signaling [interleukin (IL)-6, IL-17, IL-4), interferon γ (IFN-γ), IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)], integrin-mediated interactions [integrin subunits αITGA)4 and ITGB7], and microbiome-related factors that contribute to irAE pathology.
This exploration of modifiable pathways uncovers new opportunities to mitigate irAEs by using available antibodies (Abs) that target key inflammatory molecules across tumor types, while ideally preserving the antitumor efficacy of ICIs.
(*incl. additional corresponding authors Thomas Gajewski & Prof. Dr. Jessica Hassel)
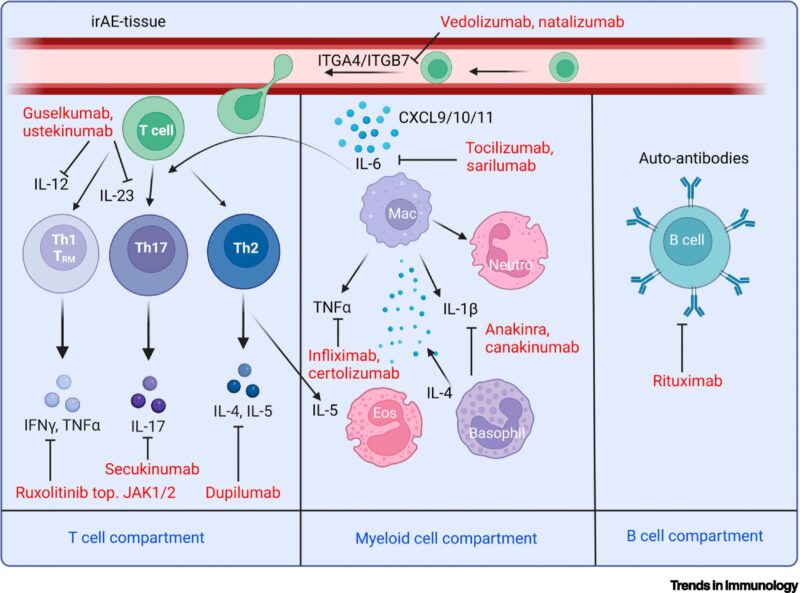
FIGURE | Cellular and molecular targets involved in immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-related toxicity | The figure also depicts the targets that might be therapeutically perturbed with clinically available antibodies. Antibodies can be directed toward various cell compartments based on the predominant cell types involved in immune-related adverse events (irAEs).
For instance, antibodies can target specific T cell subsets, such as Th1, Th17, and Th2 cells, as well as myeloid cell subsets such as macrophages. Antibodies can also target autoantibody-producing B cells. Integrin-blocking antibodies can disrupt the adhesion of circulating immune cells, potentially leading to inflammation associated with irAEs. Spheres represent secreted chemokines/cytokines.”
Targeting molecular pathways to control immune checkpoint inhibitor toxicities.
Authors: Robin Reschke, et al.



