The SMART ONE trial is the first prospective study to evaluate the feasibility, safety, and clinical outcomes of single-fraction stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) delivered using magnetic resonance-guided radiotherapy (MRgRT) for extracranial visceral tumors. Conducted across two academic centers, the study enrolled 30 patients with 32 lesions—mostly metastatic and primarily from colorectal and lung primaries—treated with a single high-dose SBRT session tailored by tumor location. Leveraging MR-linac technology for real-time imaging, respiratory gating, and online adaptive radiation therapy (ART), the trial demonstrated precise treatment delivery within 5 mm of the target, with a median in-room time of just 53 minutes. With a 1-year local control rate of 96.2%, minimal acute toxicity, and no grade ≥3 late adverse events, this trial highlights the promise of MR-guided single-fraction SBRT as a practical and effective approach for managing selected visceral tumors, particularly those near critical organs, and sets the foundation for broader adoption and future dose-escalation strategies.
Title: Stereotactic magnetic resonance-guided adaptive radiation therapy in one fraction (SMART ONE): a multi-center, single-arm, phase 2 trial
Authors: Michael. D. Chuong, MD, Kathryn E. Mittauer, PhD, Michael F. Bassetti, MD, Carolina Rojas, BS, Carri Glide-Hurst, PhD, Noah S. Kalman, MD, Martin C. Tom, MD, Muni Rubens, MBBS, MPH, PhD, Jennie Crosby, PhD, Adam Burr, MD, Ranjini Tolakanahalli, PhD, Alonso N. Gutierrez, PhD, MBA, Nema Bassiri, PhD, Minesh P. Mehta, MD, Rupesh Kotecha, MD
Published in IJROBP, March 2025
Background
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) delivers high-dose radiation in a few fractions with sub-millimeter precision. Traditionally used for inoperable early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SBRT has expanded to treat extracranial tumors and oligometastatic disease. While single-fraction SBRT has shown clinical promise—offering patient convenience, cost-effectiveness, and potential immunostimulation—it is rarely used due to imaging limitations and concerns about intrafraction motion. The advent of magnetic resonance-guided radiotherapy (MRgRT) allows for real-time tumor tracking and online adaptive radiotherapy (ART), potentially enabling safer delivery of single-fraction SBRT to visceral tumors.
Methods
SMART ONE trial is an open-label, single-arm, prospective phase 2 study that evaluated the feasibility and tolerability of single-fraction SBRT delivered via MR-linac (0.35 Tesla ViewRay MRIdian®) to visceral extracranial tumors. The primary objectives were treatment feasibility (completion within 3 working days, in-room time ≤90 minutes in ≥80% of cases, and accurate delivery within 5 mm of planned target) and tolerability (≤4 grade 3+ acute adverse events and no treatment-related grade 5 toxicity).
Study Design
30 patients (median age 69 years, range 49–90), ECOG ≤2, with inoperable primary or metastatic carcinomas in the lung, liver, adrenal gland, pancreas, kidney, or lymph nodes (≤5 cm lesions, 1–10 lesions per patient) were included in this trial
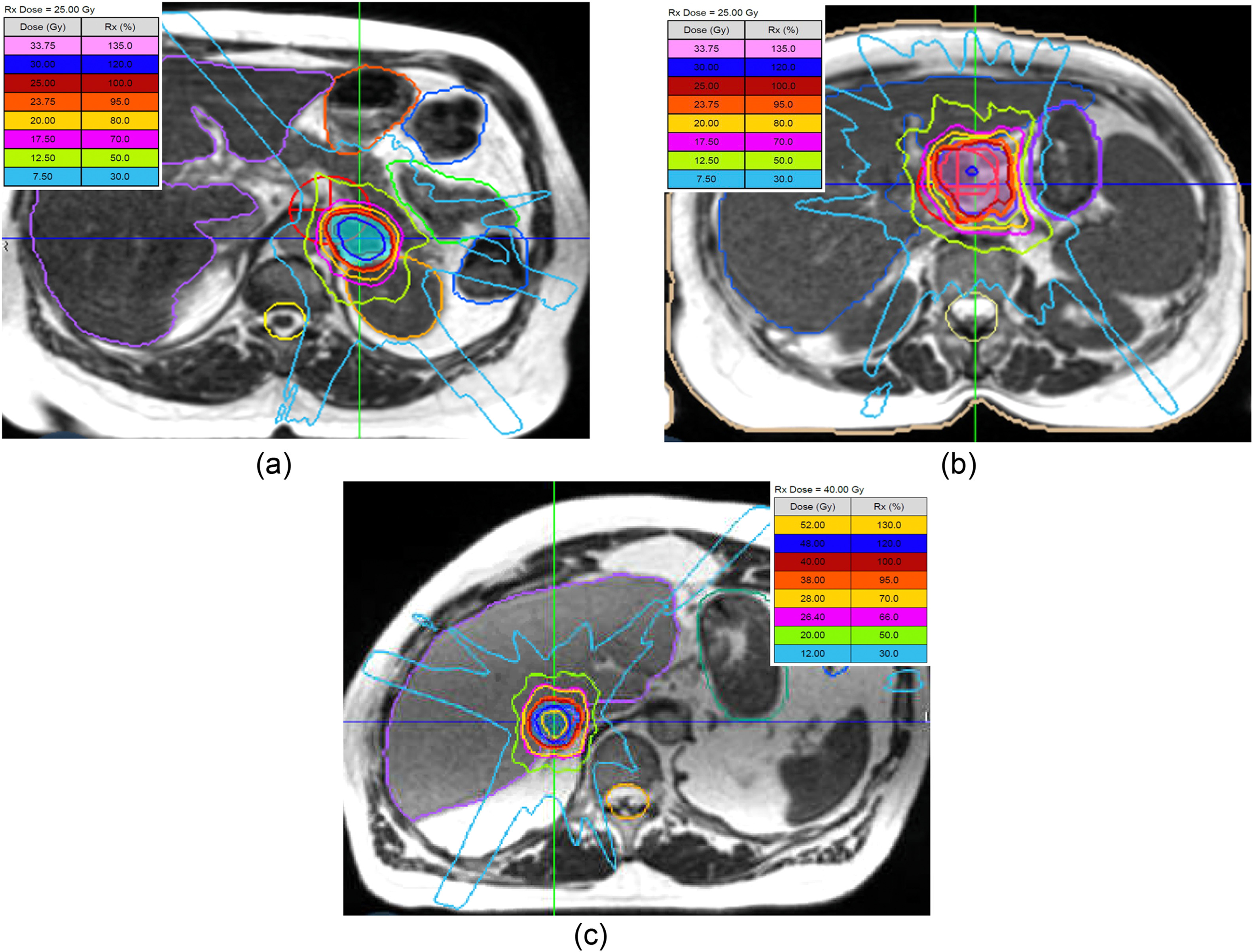
Patients received single-fraction SBRT with doses tailored by anatomic site (e.g., lung: 30–34 Gy; liver: 35–40 Gy; pancreas/kidney/adrenal/LN: 25 Gy).
Pre-treatment volumetric MRI and continuous cine-MRI during treatment with respiratory gating and optional online ART was performed and patients were followed at baseline, day of the treatment and at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months.
Results
A total of 32 lesions were treated among 30 patients, with two patients receiving SBRT to two lesions each. The vast majority of lesions (94%) were metastatic, and the most common primary tumor origins were colorectal (50%) and lung (31.3%). The median tumor diameter was 1.7 cm, with a range spanning from 1.0 to 3.9 cm.
Feasibility Outcomes
All patients successfully completed their treatment. Online adaptive radiation therapy (ART) was utilized in 43.8% of treatments, primarily for lesions located near dose-sensitive organs. In terms of procedural efficiency, the in-room time was 90 minutes or less in 87.1% of cases, with a median total in-room duration of 53 minutes (range: 39 to 195 minutes). Importantly, treatment delivery was verified to be within 5 mm of the planned target location in all cases, confirming precise tumor targeting.
Dosimetric Performance
The dosimetric outcomes were favorable across all anatomical sites.
Median GTV D95%:
- Adrenal: 30.2 Gy (BED10 = 121.4 Gy₁₀)
- LN: 29.3 Gy (BED10 = 115.2 Gy₁₀)
- Liver: 42.8 Gy (BED10 = 225.9 Gy₁₀)
- Lung: 39.5 Gy (BED10 = 195.5 Gy₁₀)
- Hotspots (≥120–130% of prescription) were confined to GTV, enhancing tumoricidal effect.
Key Findings
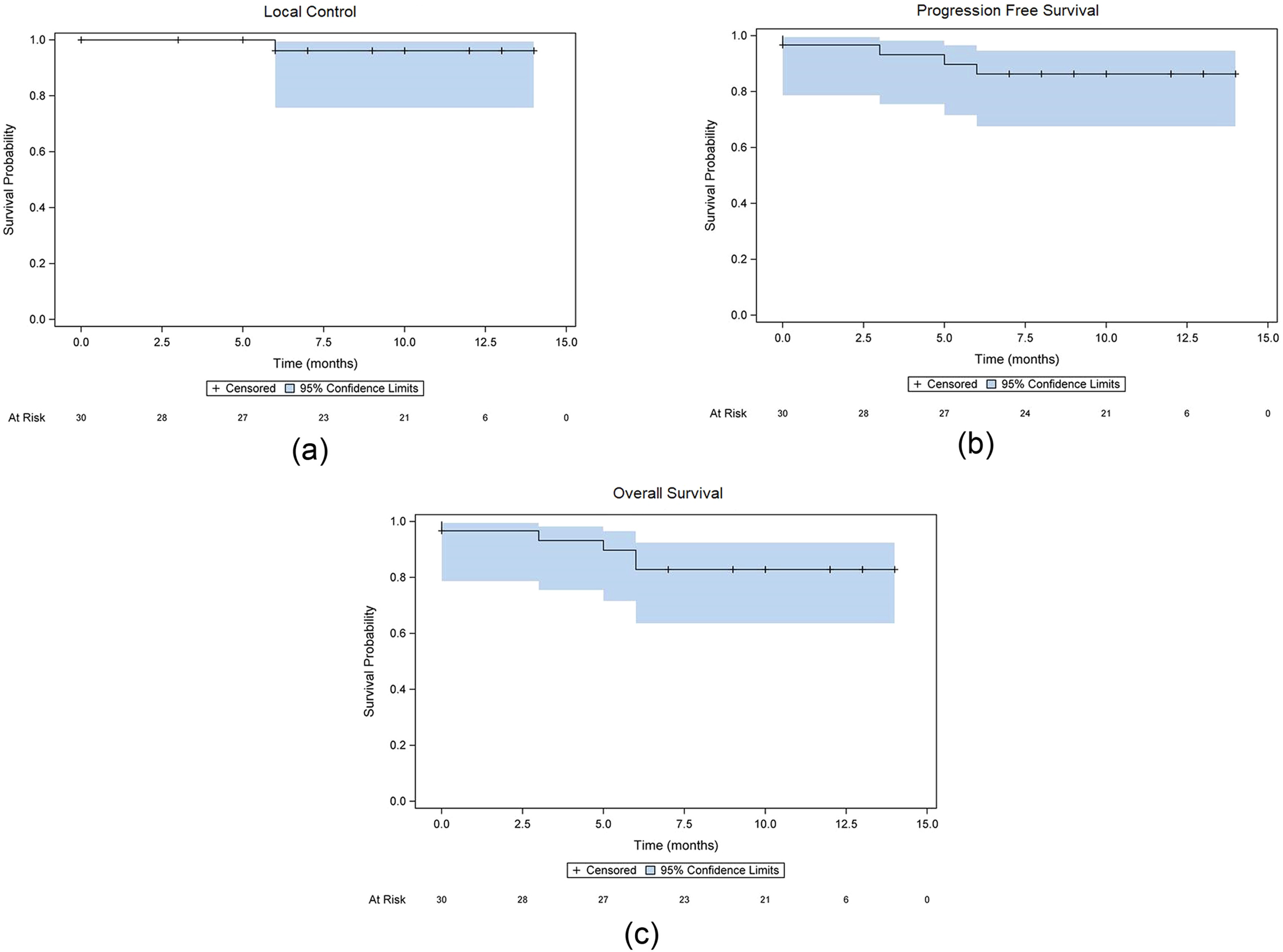
The SMART ONE trial establishes, for the first time in a prospective setting, the feasibility and safety of single-fraction MR-guided SBRT for visceral tumors. With a median treatment time under 1 hour and promising early clinical outcomes—including 96.2% 1-year LC and minimal toxicity—this trial supports broader consideration of single-fraction SBRT regimens. As MR-linacs become more widely available, future studies should explore dose escalation, particularly in non-liver abdominal targets, and define optimal patient selection criteria to further refine this evolving paradigm in radiation oncology.
- 1-year local control (LC): 96.2% (95% CI: 88.8–100%)
- 1-year progression-free survival (PFS): 82.9% (95% CI: 69.2–96.5%)
- 1-year overall survival (OS): 86.3% (95% CI: 73.8–98.8%)
- Only 1 local failure occurred in a colorectal adrenal metastasis treated with 25 Gy.
- Grade 3 acute toxicity in 3 patients (10%); only 1 possibly treatment-related (pericarditis).
- No grade 5 or late grade ≥3 toxicities were reported.
- Quality of life (FACT-G) scores were stable over time, with no significant decline across physical, emotional, or social domains.
Key Takeaway Messages
- Single-fraction SBRT using MR-guidance is safe, feasible, and efficient, even for tumors near dose-sensitive GI structures.
- Real-time imaging and online ART enabled precise tumor targeting and minimized risk of toxicity.
- Clinical outcomes at 1 year suggest that high local control can be achieved even in predominantly radioresistant tumor types.
- The approach may reduce treatment burden, enabling multiple lesions to be treated within days instead of weeks.
- Adoption of MR-linac technology could significantly expand single-fraction SBRT indications, particularly in metastatic settings.
You can read the full article here