Hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative (HR+/HER2−) advanced breast cancer (aBC) represents the most common subtype of metastatic breast cancer and remains a significant contributor to cancer-related mortality in women worldwide. The integration of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i)—palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib—into first-line therapy alongside endocrine therapy (ET) has transformed the treatment landscape, offering substantial improvements in progression-free survival (PFS) and, in some cases, overall survival (OS). Despite widespread use, direct comparative evidence from randomized trials is lacking. The PALMARES-2 study addresses this critical gap by evaluating and comparing the real-world effectiveness of these three CDK4/6 inhibitors in a large, multicenter Italian cohort of HR+/HER2− aBC patients
Title: Real-world effectiveness comparison of first-line palbociclib, ribociclib or abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy in advanced HR+/HER2- BC patients: results from the multicenter PALMARES-2 study
Authors:L. Provenzano, M.V. Dieci, G. Curigliano, M. Giuliano, A. Botticelli, M. Lambertini, G. Rizzo, R. Pedersini, M. Sirico, N. La Verde, A. Gennari, A. Zambelli, A. Toss, M. Piras, M. Giordano, B. Tagliaferri, D. Generali, D. Sartori, D. Miliziano, A. Menichetti, F. Ligorio, C. Zurlo, G. Griguolo, P.P. Berton Giachetti, V. Faso, C. Corti, E. Chiappe, S. Scagnoli8 ∙ S. Pisegna, C. Capasso, C. De Angelis, G. Arpino, C. Criscitiello, V. Guarneri∙ G. Pruneri, L. Mariani, C. Vernieri, PALMARES-2 study group
Published in Annals of Oncology, April 2025
Background
HR-positive, HER2-negative (HR+/HER2-) advanced breast cancer (aBC) is the most prevalent subtype of aBC and a leading cause of related deaths. CDK4/6 inhibitors—palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib—combined with endocrine therapy (ET) have become the first-line standard of care. While randomized trials have demonstrated the benefit of these agents individually, no large-scale, real-world comparison had been available. The PALMARES-2 study aimed to compare the real-world effectiveness of these three agents in a multicenter Italian setting.
Methods
PALMARES-2 is a retrospective/prospective, observational, multicenter study across 18 Italian cancer centers. It evaluated first-line CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy (palbociclib, ribociclib, or abemaciclib) plus ET in HR+/HER2- aBC patients between January 2016 and September 2023. Data were collected from electronic health records and standardized across centers.
Study Design
A total of 1,982 patients with HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer were included in the PALMARES-2 study. Among them, 789 (39.8%) received palbociclib, 736 (37.1%) received ribociclib, and 457 (23.1%) were treated with abemaciclib, each in combination with endocrine therapy (ET) as first-line treatment.. The median age across the cohort was 63 years, with 33% of patients having endocrine-resistant tumors, 18% being premenopausal, and 30% presenting with de novo metastatic disease. Ovarian function suppression was consistently administered in premenopausal patients.
The median follow-up for the study was 31.3 months overall, but differed by treatment: 45.7 months for palbociclib, 25.2 months for ribociclib, and 22.4 months for abemaciclib
The primary endpoint was real-world progression-free survival (rwPFS). Secondary endpoints included time to next treatment or death (TTNT-D), time to chemotherapy or death (TTC-D), and overall survival (OS). Data were adjusted using multivariable Cox regression models and inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW).
Results
The PALMARES-2 study is the first large-scale, real-world head-to-head comparison of all three CDK4/6 inhibitors in HR+/HER2- aBC. It reveals significant differences in clinical effectiveness, highlighting abemaciclib and ribociclib as superior to palbociclib in several patient subgroups. These findings support a tailored treatment approach in selecting CDK4/6 inhibitors and emphasize the value of real-world evidence in complementing RCT data to guide clinical practice.
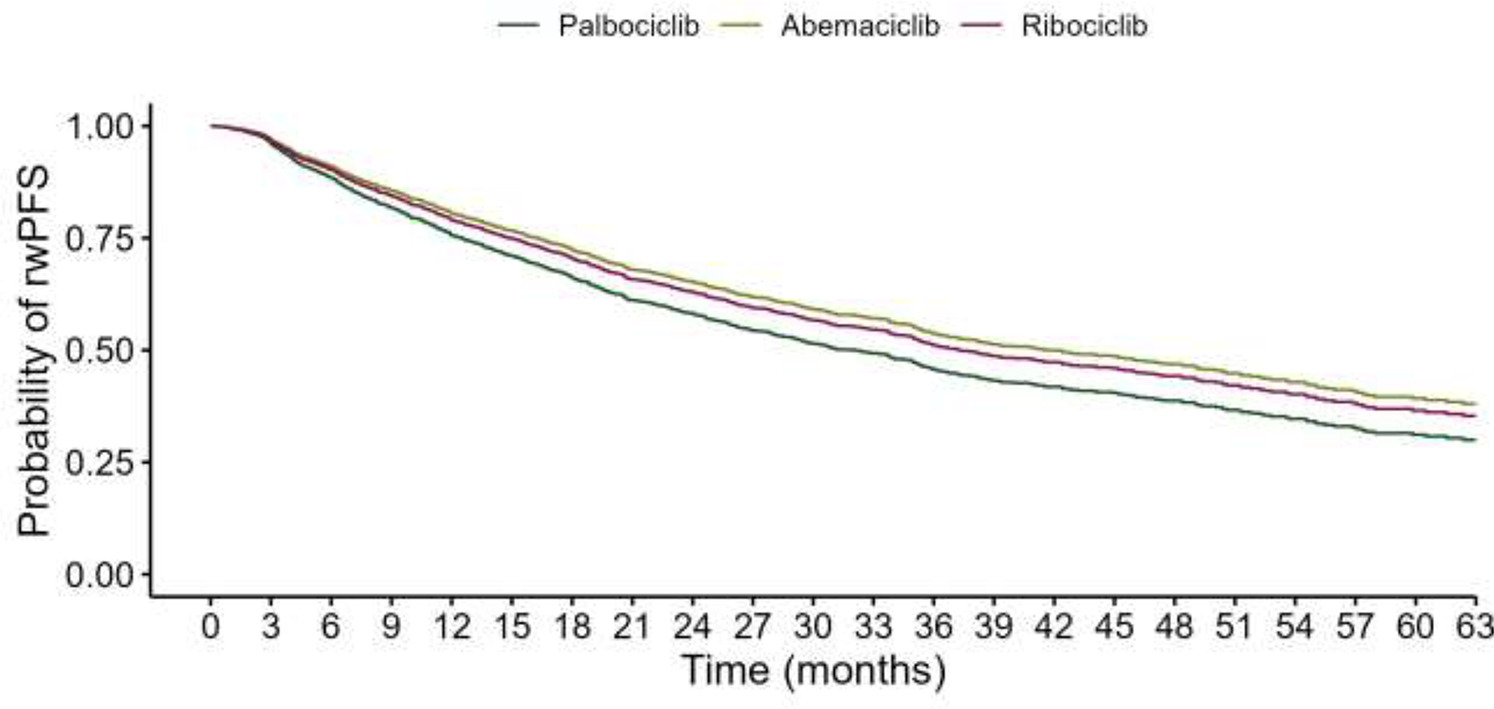
- Median rwPFS (entire cohort): 34.1 months
- Median OS: 65.9 months (data immature; 464 events)
Median follow-up: 31.3 months overall
- Palbociclib: 45.7 months
- Ribociclib: 25.2 months
- Abemaciclib: 22.4 months
Comparative Effectiveness (Multivariable Adjusted rwPFS):
- Abemaciclib vs. Palbociclib: aHR 0.76 (95% CI: 0.63–0.92, p=0.004)
- Ribociclib vs. Palbociclib: aHR 0.83 (95% CI: 0.73–0.95, p=0.007)
- Abemaciclib vs. Ribociclib: aHR 0.91 (95% CI: 0.73–1.14, p=0.425)
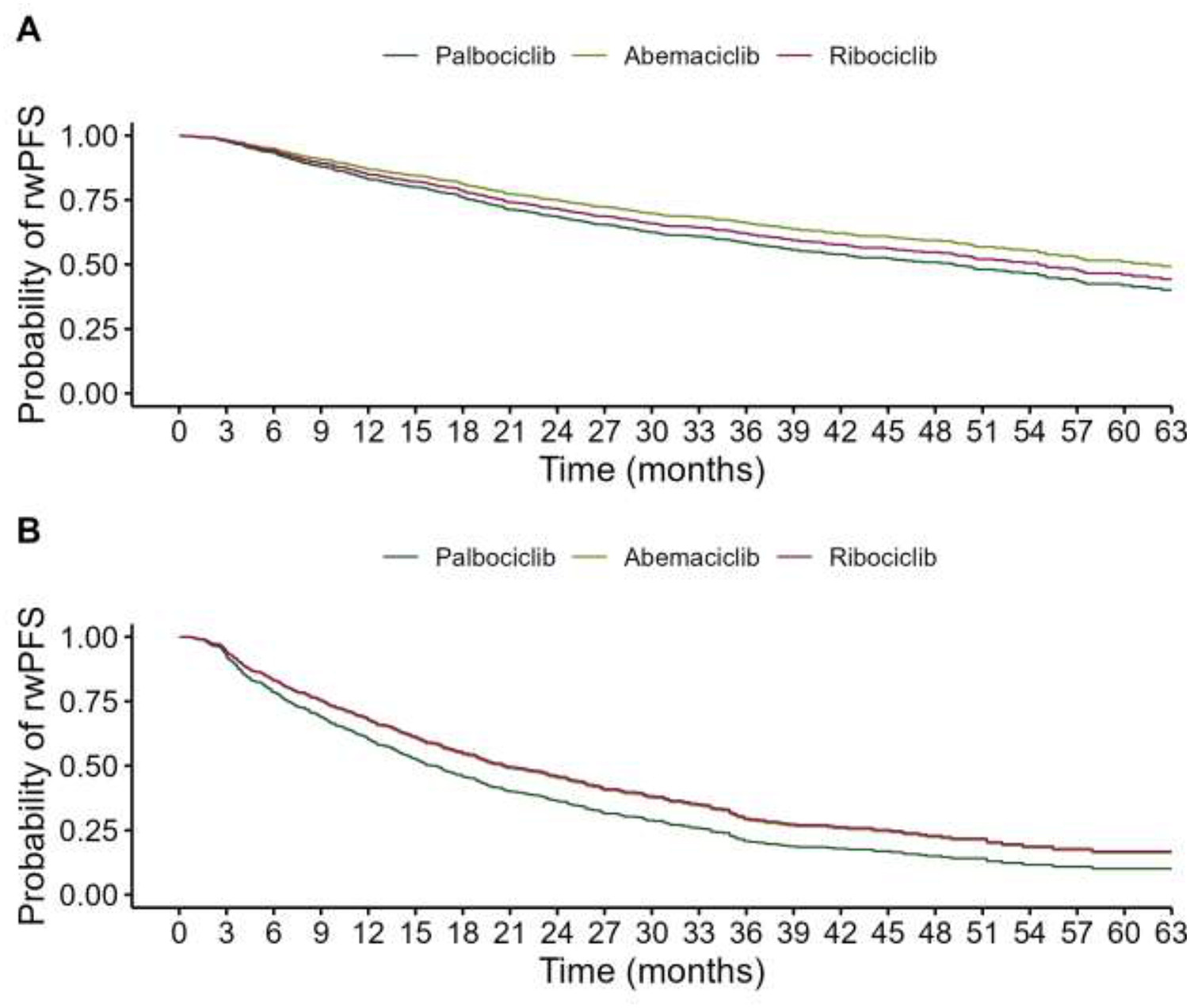
Endocrine Sensitivity Subgroups:
- Abemaciclib vs. Palbociclib: aHR 0.75 (p<0.001)
- Ribociclib vs. Palbociclib: Not significant
In endocrine-resistant disease:
- Abemaciclib vs. Palbociclib: aHR 0.77 (p=0.008)
- Ribociclib vs. Palbociclib: aHR 0.75 (p=0.034)
Secondary Endpoints:
TTNT-D:
- Abemaciclib vs. Palbociclib: aHR 0.80 (p=0.049)
- Ribociclib vs. Palbociclib: aHR 0.86 (p=0.033)
TTC-D:
- Abemaciclib: HR 0.79 (p<0.001)
- Ribociclib: HR 0.84 (p=0.016)
Exploratory OS:
- Abemaciclib: HR 0.85 (p=0.014)
- Ribociclib: HR 0.83 (p<0.001)
Key Findings
- Abemaciclib and ribociclib both demonstrated superior rwPFS over palbociclib.
- In endocrine-sensitive patients, only abemaciclib showed significant benefit.
- Subgroup advantages for abemaciclib and ribociclib include premenopausal, luminal B-like, de novo metastatic, and poor ECOG PS cohorts.
- Palbociclib remains a viable option for older patients and those with less aggressive disease (e.g., bone-only metastases).
- TTNT-D, TTC-D, and early OS data aligned with rwPFS results, reinforcing overall consistency.
Key Takeaway Messages
- Personalization Matters: Drug selection for HR+/HER2- aBC should consider patient age, disease biology, endocrine sensitivity, and comorbidities.
- Abemaciclib and Ribociclib Lead: Both agents offer a real-world survival advantage in multiple clinically relevant subgroups.
- Palbociclib Has a Role: Best safety profile; suitable for elderly or low-risk patients.
- Subgroup Data is Critical: Especially for de novo, endocrine-resistant, and luminal B-like cases.
You can read the full articl here
Written by Sona Karamyan, MD


