Tislelizumab (Tevimbra) is a PD-1 inhibitor monoclonal antibody designed to enhance the immune system’s ability to fight cancer. It has received several approvals for treating various cancers. In the U.S., the FDA approved Tevimbra in combination with chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of unresectable or metastatic HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma with PD-L1 expression ≥1% on December 27, 2024.
Additionally, it was approved for the first-line treatment of unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) with PD-L1 ≥1% on March 4, 2025. Tevimbra was previously approved as monotherapy for ESCC in patients who had received prior systemic chemotherapy. In the EU, the European Commission approved Tevimbra in combination with chemotherapy for first-line ESCC and gastric/GEJ adenocarcinoma on November 27, 2024.
While specific details about NMPA approvals in China are unavailable, Tislelizumab has been approved there for certain indications. Overall, Tislelizumab plays a significant role in treating gastric/GEJ adenocarcinoma and ESCC, both in the U.S. and EU.
Which company produced Tislelizumab?
Tislelizumab (Tevimbra) is developed by BeiGene, a global biotechnology company headquartered in Beijing, China, founded in 2010. BeiGene specializes in innovative cancer treatments, particularly in immunotherapy and targeted therapies, with a strong pipeline that includes BTK inhibitors and PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors like tislelizumab.
On January 11, 2021, Novartis signed an agreement to in-license Tislelizumab from BeiGene for $650 million upfront, plus royalties and milestone payments. The deal grants Novartis development and commercialization rights in North America, Europe, and Japan, expanding its oncology pipeline with a late-stage PD-1 inhibitor. Tislelizumab is approved for multiple cancer indications, including esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and gastric/gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma, and is being developed globally as both a monotherapy and in combination therapies.

BeiGene has expanded globally, with research, clinical, and commercial operations in North America, Europe, and Asia. It collaborates with major pharmaceutical companies and emphasizes making high-quality cancer treatments more accessible worldwide.
How does Tevimbra work?
Under normal conditions, the immune system uses T cells to detect and destroy abnormal or infected cells. However, to prevent excessive immune responses that could damage healthy tissues, the body has immune checkpoints like programmed death-1 (PD-1), a receptor found on T cells. When programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)—expressed by normal or tumor cells—binds to PD-1, it sends an inhibitory signal that reduces T-cell activity, preventing an immune attack.
Tevimbra is a monoclonal antibody that binds to PD-1, blocking its interaction with PD-L1. This prevents tumors from using the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway to evade immune detection. By lifting this “brake” on T cells, Tislelizumab restores and enhances the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. Unlike some other PD-1 inhibitors, Tislelizumab is specifically designed to reduce Fc-gamma receptor binding on macrophages, minimizing immune cell depletion and improving efficacy.
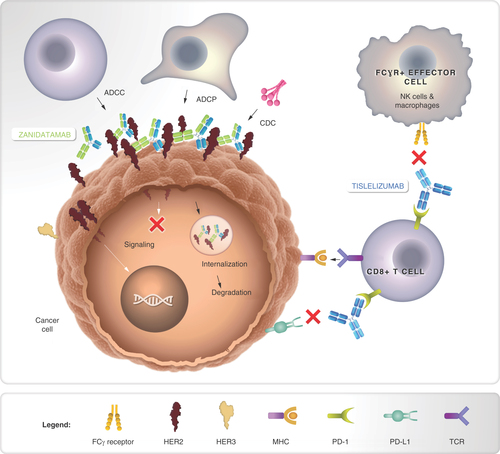
Tabernero, J., Shen, L., Elimova, E., Ku, G., Liu, T., Shitara, K., … Ajani, J. (2022). HERIZON-GEA-01: Zanidatamab + chemo ± Tislelizumab for 1L treatment of HER2-positive gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Future Oncology, 18(29), 3255–3266. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2022-0595
What Cancers Is Tislelizumab Approved to Treat?
Tislelizumab is FDA-approved for advanced gastroesophageal cancers. In February 2024, it was approved for unresectable or metastatic ESCC after prior chemotherapy. On December 27, 2024, approval expanded to HER2-negative gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma (with PD-L1 expression) as a first-line treatment with chemotherapy.
What research is behind the approval?
The FDA approvals of Tislelizumab for advanced esophageal and gastric cancers were based on pivotal clinical trials demonstrating significant survival benefits.
For esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), the approval in February 2024 was supported by the RATIONALE-302 trial, a global phase III study comparing Tevimbra monotherapy to standard chemotherapy in 512 patients with previously treated, unresectable, or metastatic ESCC. The trial showed that Tislelizumab improved overall survival (OS) compared to chemotherapy, with a median OS of 8.6 months vs. 6.3 months (HR = 0.70; p = 0.0001), leading to its approval for patients who had already undergone systemic chemotherapy.
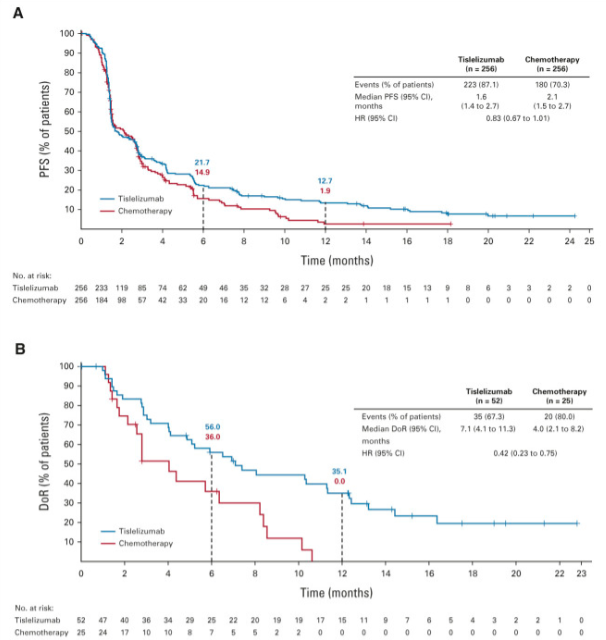
The RATIONALE-306 trial, published in The Lancet Oncology in April 2023, evaluated Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The study showed a significant survival benefit, with a median overall survival (OS) of 17.2 months versus 10.6 months in the placebo group (HR 0.66). Progression-free survival (PFS) was 7.3 months compared to 5.6 months (HR 0.62), confirming tislelizumab’s potential to improve outcomes for ESCC.
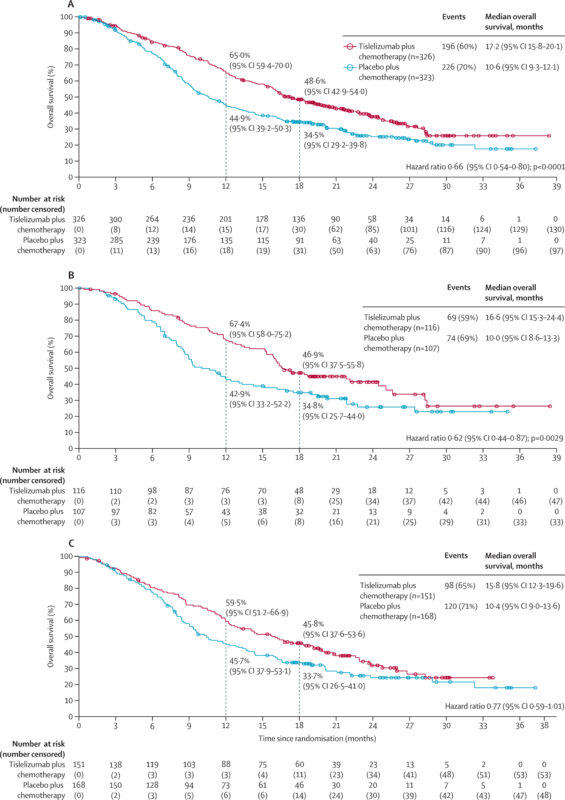
The approval for unresectable or metastatic HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma on December 27, 2024, was based on the RATIONALE-305 trial. This phase III, double-blind study evaluated Tislelizumab combined with platinum- and fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy as a first-line treatment. The FDA approved Tevimbra plus chemotherapy for first-line treatment of PD-L1+ HER2-negative gastric and GEJ adenocarcinoma. The RATIONALE-305 trial showed improved overall survival (15.0 vs 12.9 months, HR 0.80, P = 0.0011) and higher response rates (48% vs 41%) vs chemotherapy alone.
These trials provided strong clinical evidence that Tislelizumab enhances immune response and improves survival outcomes, establishing it as a promising immunotherapy for advanced gastroesophageal cancers.
Learn more about Esophageal Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, Stages, Diagnosis and Treatment on OncoDaily.
Tislelizumab Combinations and Treatment Outcomes
Tislelizumab, an anti-PD-1 antibody, has demonstrated significant survival benefits in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) through key clinical trials.
🔹 Second-Line Treatment (RATIONALE-302):
Tevimbra monotherapy improved overall survival (OS) compared to chemotherapy in advanced ESCC (median OS: 8.6 vs. 6.3 months; HR 0.70). It also showed a better response rate and fewer severe adverse events.
🔹 First-Line Treatment (RATIONALE-306):
The combination of Tevimbra with chemotherapy provided a significant OS advantage over chemotherapy alone (median OS: 17.2 vs. 10.6 months), reducing the risk of death by 34%.
Tislelizumab side effects and its management
Tevimbra is generally well-tolerated but may cause side effects ranging from mild to severe.
Among the common side effects, patients may experience fatigue, anemia, muscle pain, cough, nausea, diarrhea, and loss of appetite. Additionally, changes in liver enzyme levels, high blood sugar, thyroid dysfunction (both hypo- and hyperthyroidism), and skin rashes can occur. While these symptoms are often manageable, they require routine monitoring and supportive care to prevent complications.
Some less common side effects include shortness of breath, dizziness, joint pain, kidney dysfunction, and peripheral neuropathy. A subset of patients may also develop immune-related adverse events, affecting critical organs such as the lungs (pneumonitis), intestines (colitis), liver (hepatitis), or endocrine glands. These immune-related toxicities require prompt identification and intervention to prevent serious complications.
Serious adverse effects, though rare, include severe infusion reactions, myocarditis, and neurological complications, which necessitate immediate medical attention. Failure to address these issues quickly can lead to life-threatening consequences.
The management of tevimbra-related side effects primarily involves regular monitoring, supportive care, and dose adjustments as needed. Immune-related toxicities may require corticosteroids or immunosuppressive therapy, depending on severity. Early recognition and timely intervention are crucial in mitigating complications and ensuring continued therapy with minimal disruption to the patient’s quality of life.
What is the Recommended Dosage of Tislelizumab?
Tevimbra is available as a 10 mg/mL injectable solution. The recommended dose is 200 mg IV every three weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. For esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), it is used with platinum-based chemotherapy as a first-line treatment or as monotherapy for previously treated patients. In gastric and gastroesophageal junction (G/GEJ) cancer, it is combined with platinum and fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy.
How is Tevimbra administered?
Tevimbra is administered via IV infusion in 0.9% NaCl. The solution should be clear to slightly yellow; discard if discolored or contains particles. Gently mix without shaking. Withdraw 20 mL from two vials and dilute to a final concentration of 2-5 mg/mL.
The first infusion is given over 60 minutes, with subsequent doses potentially over 30 minutes if tolerated. Use a 0.2 or 0.22-micron filter and avoid coadministration with other drugs. Store vials at 2-8°C without freezing. Once diluted, use within 4 hours at room temperature or 20 hours if refrigerated.

Learn more about Stomach Cancer: Symptoms and Causes, Types, Diagnosis and Treatment on OncoDaily.
What to Avoid During Tislelizumab Treatment?
During Tislelizumab treatment, patients should avoid immunosuppressive medications like corticosteroids, as they may reduce the drug’s effectiveness. Live vaccines should also be avoided due to the risk of infection. Additionally, caution is advised with other medications that can impact immune function. Patients should report any signs of infection, organ inflammation, or autoimmune reactions to their doctor. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not use Tislelizumab due to potential harm to the baby.
Tislelizumab effectiveness over time
Tislelizumab has demonstrated effectiveness in several clinical trials, improving overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) in various cancers.
Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC)
- RATIONALE-302 (Second-line Treatment): Tevimbra improved OS (8.6 vs. 6.3 months, HR 0.70) compared to chemotherapy, with better response rates and fewer severe adverse events.
- RATIONALE-306 (First-line Treatment): When combined with chemotherapy, it significantly improved OS over chemotherapy alone (17.2 vs. 10.6 months, HR 0.66).
Gastric/Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma (G/GEJ)
- RATIONALE-305 (First-line Treatment): Tevimbra plus chemotherapy increased median OS to 15.0 months versus 12.9 months with chemotherapy alone (HR 0.80), along with improved PFS (6.9 vs. 5.9 months, HR 0.78).
While these trials confirm Tislelizumab’s benefit, responses may diminish over time due to acquired resistance, emphasizing the need for ongoing monitoring and combination strategies.
Ongoing trials with Tevimbra
Tevimbra, a PD-1 inhibitor, is being investigated in multiple clinical trials across various cancer types. In advanced solid tumors, a Phase 1-2 study (BGB-900-101) is evaluating the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary antitumor activity of the anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody BGB-A333 alone and in combination with Tislelizumab.
In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), a Phase 2 umbrella study (NCT05577702) is assessing the efficacy, safety, and pharmacodynamics of Tislelizumab monotherapy and combination therapies as neoadjuvant treatment in resectable Stage II-IIIA NSCLC. In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), a Phase 2, multi-arm study (NCT05909904) is investigating Tislelizumab in combination with investigational agents as a first-line treatment for recurrent or metastatic HNSCC.
For pancreatic cancer, a neoadjuvant study (NCT05604560) is exploring Tislelizumab with SX-682 in resectable pancreatic cancer. In bladder cancer, a single-arm, open-label trial (NCT05328336) is evaluating the safety and efficacy of Tislelizumab with nab-paclitaxel as perioperative treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer before cystectomy or complete transurethral resection. These studies aim to expand the therapeutic applications of Tislelizumab and provide insights into its efficacy across different malignancies.
Written by Mariam Khachatryan, MD
FAQ
What is Tislelizumab ?
Tislelizumab, marketed as Tevimbra, is a PD-1 inhibitor monoclonal antibody designed to help the immune system recognize and fight cancer cells.
How does Tislelizumab work in cancer treatment?
Tislelizumab blocks the PD-1 receptor, preventing cancer cells from evading immune detection, and thereby enhancing the immune response against tumors.
Which types of cancer is Tislelizumab approved to treat?
Tislelizumab is approved for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma, either alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
What are the most common side effects of Tislelizumab?
Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, decreased appetite, rash, and immune-related reactions such as pneumonitis and colitis.
How is Tislelizumab administered?
It is given as an intravenous (IV) infusion every 3 weeks, with the first infusion typically over 60 minutes and subsequent infusions possibly shortened to 30 minutes if well tolerated.
Can Tislelizumab be used in combination with other cancer treatments?
Yes, it is often combined with chemotherapy for certain cancers, such as gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.
Where is Tislelizumab approved for use?
Tislelizumab has been approved in the United States (FDA), China (NMPA), and the European Union (EMA) for different cancer indications.