Iván R. González: The NEOpredict-Lung study represents an importantevolution in the treatment of resectable NSCLC
Iván R. González, Medical Oncologist at Comprehensive Oncology Center, Hospital Ángeles Puebla, shared a post on X/Twitter:
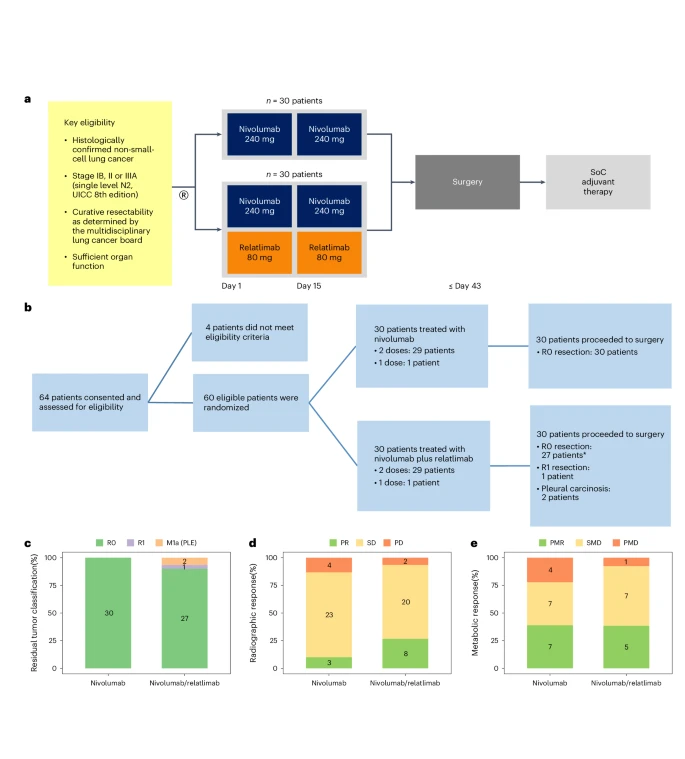
“The NEOpredict-Lung study represents an importantevolution in the treatment of resectable NSCLC, evaluating the feasibility and safety of preoperative combined treatment of nivolumab and relatlimab. The selection of this therapeutic approach was based on the premise that co-modulation of PD-1 and LAG-3-mediated immune pathways could enhance antitumor responses and improve clinical outcomes in patients with stage IB, II, and IIIA NSCLC.
With a cohort of 60 treatment-naïve patients with no biomarker selection, this randomized phase 2 trial demonstrated the feasibility of surgery in all cases, with a curative resection rate of 95%.
Pathologic and radiographic findings underscore the efficacy of this combination, with pathologic responses observed in 27% of patients treated with nivolumab and 30% of those receiving nivolumab and relatlimab. The impressive pathologically complete resection rate of 100% in the nivolumab group and 90% in the nivolumab and relatlimab group corroborates the efficacy of these treatments in completely removing the tumor and affected lymph nodes.
In addition, the results at 12 months show a disease-free survival of 89% and an overall survival of 93% in the nivolumab group, while in the nivolumab and relatlimab group, even more encouraging rates of 93% and 100% were recorded, respectively. Importantly, the safety of both therapies was acceptable, with grade ≥3 adverse events reported in 10% and 13% of patients, suggesting a favorable tolerability profile.
These results are consistent with the potential clinical and biological benefit of dual inhibition of PD-1 and LAG-3 pathways, suggesting a promising new therapeutic strategy to improve outcomes in this NSCLC patient population”
Source: Iván R. González/X